Secure Email Server Guide: Build Bulletproof Email Systems

Understanding What Makes Email Servers Truly Secure
A secure email server isn't just about sending and receiving messages. It's about protecting your sensitive information from increasingly sophisticated threats. With numerous providers touting their security features, it's crucial to discern true protection from marketing hype. Let's explore the core components of a truly secure email server and why they're essential.
Essential Security Layers
A truly secure email server employs several key security layers working in concert:
-
Authentication Protocols: These protocols verify the identities of users and servers, ensuring only authorized access to your email. Two-factor authentication adds another layer of protection, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain access even with a compromised password.
-
Encryption Standards: Encryption scrambles email content, rendering it unreadable to anyone intercepting it. Transport Layer Security (TLS) encrypts data between servers, while end-to-end encryption ensures only the sender and recipient can decrypt the message. Robust encryption algorithms are critical for protecting against eavesdropping and data breaches.
-
Monitoring Systems: Continuous monitoring of email traffic for suspicious activity is vital. This includes analyzing logs, detecting unusual patterns, and implementing intrusion detection systems like Snort. Proactive monitoring helps identify and mitigate threats before they cause damage.
Why Traditional Email Systems Fall Short
Traditional email systems often lack the comprehensive security features needed to combat modern threats. They may use outdated protocols, weak encryption, or insufficient monitoring. This leaves them open to attacks like:
-
Phishing: Phishing emails try to trick users into revealing sensitive information. A secure email server with robust spam filtering and anti-phishing measures can greatly reduce this risk.
-
Malware: Malware can spread through email attachments. Secure email servers use advanced malware detection and scanning to identify and quarantine these threats.
-
Spoofing: Spoofing involves forging the sender's address. Strong authentication in secure email servers helps prevent spoofing and verifies email authenticity.
This increasing need for robust email security is reflected in the market. The global email security market, valued at USD 4.68 billion in 2024, is projected to reach USD 10.68 billion by 2032. This growth is fueled by increasingly frequent and complex threats like ransomware and phishing. Learn more about the email security market
Building a Secure Email Fortress
Choosing a secure email server involves evaluating different solutions and deployment models. Consider factors such as:
-
Hosted vs. On-Premises: Hosted solutions offer convenience and scalability, while on-premises solutions provide more control.
-
Vendor Reputation: Choose a vendor with a proven history of delivering secure email services.
-
Compliance: Ensure the solution complies with relevant industry regulations and data privacy laws like GDPR.
By focusing on these essential security layers and understanding the evolving threat landscape, you can build an email server that truly protects your communications. This requires a strategic approach that goes beyond basic measures and incorporates advanced protection mechanisms. Investing in robust email security is an investment in the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your data.
Mastering Encryption Methods That Actually Protect You

A truly secure email server depends heavily on robust encryption to safeguard your data. But what does that actually entail? This section breaks down the essential encryption methods you should understand to make informed decisions about your email security. We'll delve deeper than simple definitions and explore how these methods function in practice, comparing their strengths and weaknesses.
Understanding the Core Encryption Methods
Several key encryption methods work in concert to secure a secure email server:
-
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): Think of sending a sealed letter that only the intended recipient can open. E2EE operates similarly, encrypting the message on the sender's device and decrypting it only on the recipient's device. This prevents intermediaries, including the email provider, from accessing the message content.
-
Encryption at Rest: This method protects your emails while they are stored on the server. It's like safeguarding your letters in a locked safe. Even if someone gains access to the server, the encrypted emails remain unreadable without the proper decryption key.
-
Transport Layer Security (TLS): TLS encrypts the connection between email servers. Imagine this as sending your sealed letter via a secure courier service. It prevents eavesdropping while the message is in transit between servers.
Evaluating Encryption Strength
Not all encryption methods provide the same level of protection. Understanding how security professionals assess encryption strength is vital for selecting a secure email server. Key factors include:
-
Algorithm Strength: The algorithms used for encryption are continually being tested and refined. Modern, well-vetted algorithms, such as AES-256, are currently considered highly secure.
-
Key Management: How encryption keys are generated, stored, and managed is as critical as the algorithm itself. Secure key management practices are essential for preventing unauthorized key access.
-
Implementation: Even the strongest algorithms can be compromised by flawed implementation. A secure email server must implement encryption correctly to ensure maximum effectiveness.
Emerging Encryption Technologies
The field of encryption is constantly evolving. While established methods like TLS and AES are currently deemed secure, new technologies are continually under development. Staying informed about these advancements is important for choosing an email server that offers long-term security. For more insights, read: How to master secure email. This constant evolution is reflected in the market itself: the email encryption market reached $7.75 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $9.49 billion in 2025, demonstrating a CAGR of 22.4%. This growth is fueled by rising concerns about data privacy and compliance regulations. Explore this topic further here.
Choosing Encryption That Works for You
Selecting the appropriate encryption methods for your secure email server depends on your specific needs and security requirements. For highly sensitive information, E2EE is crucial. For general email security, a combination of at-rest encryption and TLS is typically sufficient. Understanding these methods and their relative strengths is key to making well-informed decisions about protecting your communications. Typewire offers robust encryption features to ensure your emails remain private and secure.
Choosing Your Secure Email Server Solution Wisely
Selecting the right secure email server is a crucial decision for any individual or organization prioritizing data privacy and security. With numerous options available, careful evaluation is essential to pinpoint the best fit for your specific needs. This involves understanding different deployment models, their costs and benefits, and the key security features to consider. Let's explore the factors that empower informed decision-making.
Hosted vs. On-Premises Solutions
One of the first choices you'll face is between a hosted and an on-premises secure email server. Each option presents distinct advantages and disadvantages:
-
Hosted Secure Email Servers: These solutions are managed by a third-party provider, relieving you of server maintenance and administration. This is often a more cost-effective choice, especially for smaller businesses. Providers manage security updates, backups, and infrastructure, allowing you to concentrate on core operations. However, you have less direct control over the server environment.
-
On-Premises Secure Email Servers: On-premises solutions give you complete control over your server and its security configurations. This can be advantageous for organizations with stringent compliance requirements or unique security needs. However, setup and maintenance require significant technical expertise. This option also involves higher initial costs for hardware and software, along with ongoing maintenance expenses.
Key Features to Look For
Whether you opt for hosted or on-premises, certain security features are fundamental to any secure email server:
-
Strong Encryption: Encryption forms the bedrock of email security. Seek solutions offering end-to-end encryption, encryption at rest, and TLS encryption in transit. These measures safeguard your emails, ensuring confidentiality and protection against unauthorized access.
-
Robust Authentication: Strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication, are vital for verifying user identities and preventing unauthorized access. This adds an extra layer of security, significantly hindering attackers' attempts to compromise your email accounts.
-
Advanced Threat Protection: Secure email servers should incorporate advanced threat protection features, including spam filtering, anti-phishing measures, and malware detection. These features help block malicious emails from reaching your inbox, protecting your systems from malware infections.
-
Compliance and Auditing: If your organization must adhere to compliance regulations, ensure the chosen email server meets those requirements. Features like audit trails and data retention policies are crucial for demonstrating compliance and preserving data integrity. You might be interested in: Top Benefits of Encrypted Email.
Making the Right Choice
The infographic below provides a decision-making framework for choosing a secure email server based on your technical expertise and budget:
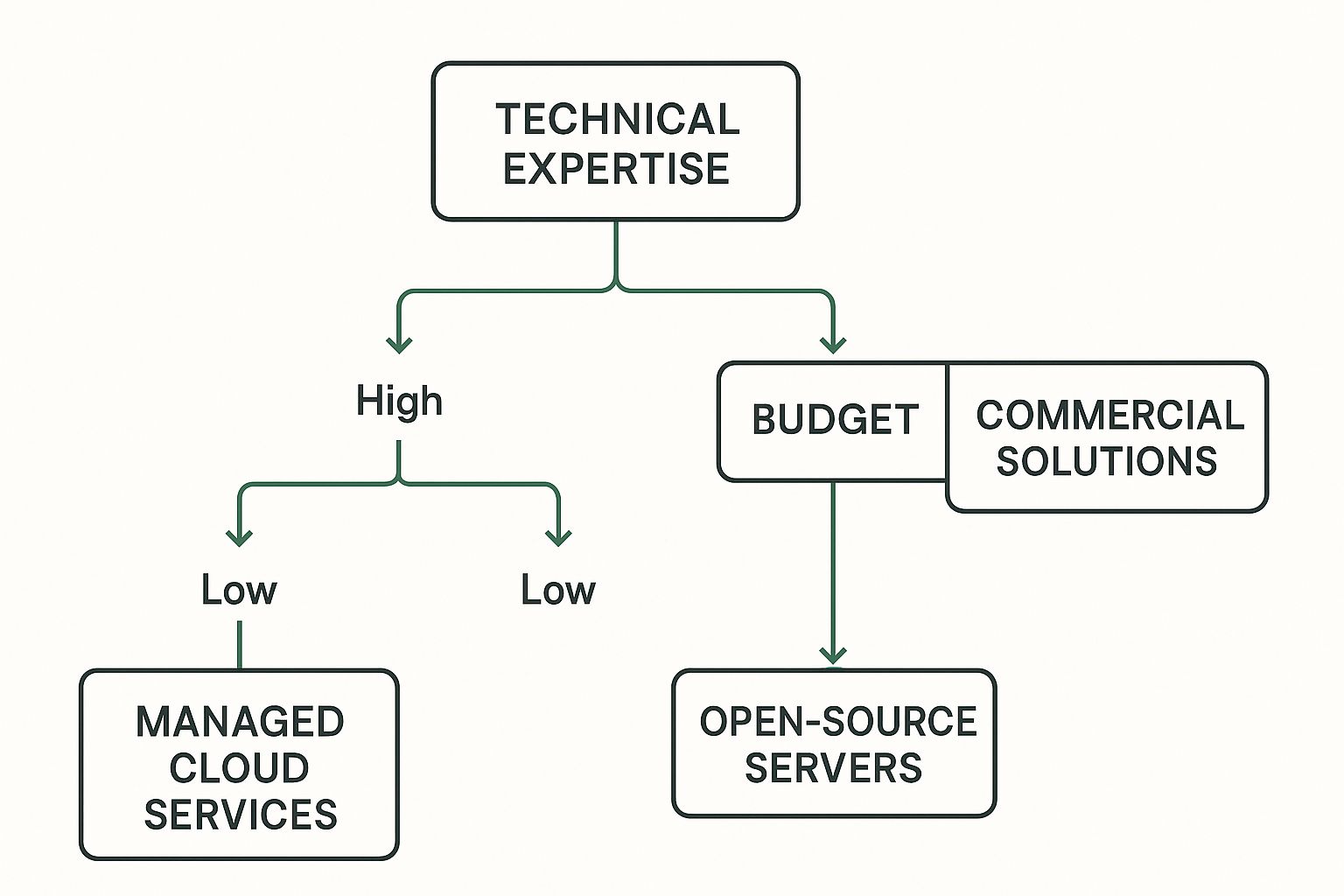
The infographic suggests that organizations with high technical expertise and a substantial budget might choose commercial solutions, while those with limited technical expertise might consider managed cloud services. Open-source servers could be a suitable option for those with high technical expertise but a limited budget. The ideal secure email server depends on your specific situation. Carefully consider your needs, available resources, and security requirements before making a decision. Platforms like Typewire offer a balance of security, control, and ease of use across various plans, accommodating diverse needs and technical expertise.
To further assist in your decision-making process, the following table compares several popular secure email server solutions:
To help you further evaluate your options, let's look at a comparison of popular secure email solutions:
Secure Email Server Solutions Comparison
| Solution Type | Security Features | Best For | Cost Range | Compliance Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ProtonMail | End-to-end encryption, zero-access encryption | Privacy-focused individuals | Free – Paid | GDPR, Swiss Privacy Laws |
| Tutanota | End-to-end encryption, open-source | Security-conscious users | Free – Paid | GDPR |
| Mailfence | End-to-end encryption, digital signatures | Businesses, individuals requiring advanced security | Free – Paid | GDPR |
| Posteo | End-to-end encryption, anonymous registration | Privacy-focused users | Paid | GDPR |
| Microsoft 365 | Encryption in transit, at rest, data loss prevention | Businesses, large organizations | Paid | HIPAA, GDPR, others |
| Google Workspace | Encryption in transit, at rest, phishing protection | Businesses, individuals | Paid | HIPAA, GDPR, others |
| Self-Hosted (e.g., Mail-in-a-Box) | Customizable security features | Technically proficient users, organizations | Varies based on infrastructure | Dependent on configuration |
This table highlights key differences in security features, target users, cost, and compliance support, allowing you to compare and select the solution that best aligns with your specific needs.
Implementation Strategies That Prevent Common Failures

Moving from the planning phase to actually deploying a secure email server can be a complicated process. This section outlines key implementation strategies that separate successful projects from those that run into problems. We'll cover a step-by-step guide, common pitfalls, and the techniques experienced administrators use to overcome technical hurdles.
Configuring Security Settings for a Secure Email Server
A robust secure email server depends on correctly configured security settings. This includes implementing strong authentication protocols, like two-factor authentication, and requiring secure passwords. Encrypting data, both in transit with TLS and at rest, is also vital for protecting email content. These steps are fundamental to preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding sensitive information.
Implementing Effective Authentication Systems
Authentication is the first line of defense for your secure email server. Going beyond basic username/password authentication by implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances security. MFA requires users to present multiple forms of identification, making it much more difficult for attackers to compromise your server. This added layer of security is especially important considering the rise of phishing attacks and password breaches.
Establishing Proactive Monitoring and Threat Detection
Monitoring your secure email server for suspicious activity is essential for identifying and mitigating threats. Implementing intrusion detection systems and regularly reviewing server logs helps detect unusual activity and potential attacks before they escalate. Setting up automated alerts to notify administrators of critical events ensures timely responses to security incidents.
Common Implementation Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Many secure email server implementations encounter problems due to avoidable mistakes. Some of the most common issues include:
- Weak Passwords: Implement and enforce strong password policies and educate users about good password hygiene.
- Outdated Software: Regularly update your secure email server software and operating system with the latest security patches.
- Ignoring Security Best Practices: Adhere to established security guidelines for server configuration, including proper firewall rules and access controls.
- Insufficient Testing: Thoroughly test your secure email server in a controlled environment before deploying it to identify and address any configuration problems.
Handling Technical Challenges
Deploying a secure email server presents several technical challenges that experienced administrators address proactively:
- Firewall Configuration: Proper firewall configuration is essential. It should allow legitimate email traffic while blocking unauthorized attempts to access the server.
- Certificate Management: Obtain and properly manage SSL certificates from a trusted Certificate Authority to ensure secure, encrypted connections.
- User Onboarding: A smooth onboarding process for new users is vital. Ensure they understand and can use the secure email server effectively.
Successfully addressing these technical aspects is key to building a secure and dependable email system. The email security solutions market is experiencing rapid growth, valued at USD 18.5 billion in 2024 and projected to reach USD 24 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 4.4%. This growth is fueled by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, highlighting the importance of robust email security. For more detailed statistics, see this report.
Troubleshooting and Performance Optimization
Even with careful planning, problems can surface after deployment. Having effective troubleshooting strategies in place is crucial for quick resolution. This includes analyzing logs, monitoring server performance, and using diagnostic tools. Optimizing server performance is an ongoing effort to ensure your secure email server remains both secure and efficient. Platforms like Typewire offer robust support and resources for tackling technical challenges and optimizing performance. This proactive approach ensures your secure email server remains a reliable and well-protected communication platform.
Building Threat Detection That Actually Works
A truly secure email server needs more than just strong encryption and authentication. It requires a robust threat detection system that proactively identifies and neutralizes attacks. Many organizations struggle with alert fatigue, where a high volume of alerts makes it difficult to separate real threats from false positives. This section explores building a threat detection system for your secure email server that minimizes noise and maximizes protection.
Advanced Detection Methods
Effective threat detection depends on a combination of methods, each with a specific role in identifying malicious activity:
-
Behavioral Analysis: This method examines email traffic patterns to find anomalies. A sudden increase in emails from a single sender, or many emails with suspicious attachments, could signal an attack. This approach helps uncover previously unknown threats that might slip past traditional signature-based systems.
-
Machine Learning Applications: Machine learning algorithms analyze large amounts of email data to learn normal communication patterns and identify deviations suggesting malicious intent. This method adapts to evolving threats, constantly refining its detection capabilities. This results in more accurate detection and fewer false positives.
-
Signature-Based Detection: This traditional approach relies on identifying known malicious signatures, such as specific malware code or phishing email templates. While valuable, signature-based detection alone isn't enough. It requires regular updates to remain effective against new threats.
Integrating Threat Intelligence
Threat intelligence feeds provide crucial information about emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Integrating these feeds into your threat detection system greatly improves its accuracy and effectiveness. This offers current data on new malware, phishing campaigns, and other attack vectors, enabling proactive defense. Typewire incorporates threat intelligence for comprehensive email server protection.
Automating Response Systems
An automated response system significantly improves the ability to contain and mitigate threats quickly. This involves pre-defining specific actions when threat thresholds are met. Automatically quarantining emails with suspected malware or blocking emails from known malicious IP addresses can substantially reduce an attack's impact.
Real-World Attack Scenarios
Understanding real-world attack scenarios is vital for building effective threat detection. Consider these examples:
-
Spear Phishing: This targeted phishing attack often impersonates a trusted individual to steal credentials or install malware. Effective detection requires identifying spoofed email addresses, suspicious links, and unusual communication patterns.
-
Malware Delivery: Attackers use email attachments to deliver malware. Strong attachment scanning and malware detection are essential to identify and quarantine these threats.
-
Business Email Compromise (BEC): BEC attacks often compromise a legitimate email account to initiate fraudulent financial transactions. Detecting BEC requires careful analysis of email content, watching for unusual payment requests or banking information changes.
By understanding these common attack vectors, you can design a threat detection system to address the specific risks your server faces. This includes configuring security settings to identify and block these attacks, protecting sensitive information. Choosing a secure email server solution like Typewire provides built-in robust threat detection. This allows you to focus on your core business while staying protected against a range of attacks. Typewire uses advanced techniques like behavioral analysis and machine learning to identify threats and minimize false positives.
Navigating Compliance Without Compromising Security

Handling sensitive data requires robust compliance measures, and your secure email server is no different. However, true security shouldn't be sacrificed for the sake of ticking compliance boxes. This section explores how to effectively meet regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX while maintaining a truly secure email environment. It's about finding the right balance – using regulations to enhance, not diminish, your overall protection.
Understanding Compliance Requirements
Several regulations directly impact how organizations manage email security, often dictating specific security measures and best practices. Let's look at a few key examples:
-
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): This EU regulation emphasizes data privacy and protection for individuals within the European Union. For organizations handling personal data of EU citizens, the GDPR mandates robust data security measures like encryption and access controls.
-
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): HIPAA governs the protection of sensitive patient health information in the US. It requires healthcare providers and related organizations to implement strict security measures for electronic protected health information (ePHI), including email communications. For therapists seeking secure email solutions, consider this resource: HIPAA Compliant Email for Therapists.
-
SOX (Sarbanes-Oxley Act): SOX focuses on financial reporting and corporate governance for publicly traded companies in the US. While not solely focused on email security, SOX mandates strong internal controls and comprehensive audit trails, which can significantly influence how organizations handle email archiving and retention.
To further clarify the email security implications of these regulations, the table below offers a concise overview:
Introduction to Email Security Compliance Table: The following table outlines the key requirements, impact on email security, potential penalties, and typical implementation timelines for major compliance regulations. This information helps organizations understand the necessary steps to achieve and maintain compliance.
| Regulation | Key Requirements | Email Security Impact | Penalties | Implementation Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Data protection by design and default, data breach notification, data subject rights | Requires strong encryption, access controls, and data retention policies for emails containing personal data | Up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover | Ongoing since May 25, 2018 |
| HIPAA | Confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI, security risk analysis, security awareness training | Requires robust secure email solutions, encryption, and access controls for emails containing ePHI | Tiered penalty system ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, up to $1.5 million per year for each violation category | Ongoing since 1996, with various updates and enforcement deadlines |
| SOX | Internal controls over financial reporting, independent audits, CEO and CFO certification | Influences email archiving and retention policies to ensure data integrity and auditability | Fines up to $5 million and imprisonment up to 20 years | Ongoing since 2002, with ongoing compliance requirements |
Key Insights from Email Security Compliance Table: Achieving compliance with these regulations requires a proactive approach to email security. Organizations must implement strong technical controls, establish clear policies and procedures, and maintain ongoing awareness and training programs.
Enhancing Security Through Compliance
Compliance measures can significantly strengthen email security. For example, the GDPR's emphasis on data protection necessitates strong encryption. This directly benefits security by protecting email content from unauthorized access. HIPAA's stringent requirements for ePHI protection also encourage healthcare providers to adopt robust secure email gateways and other solutions, improving their overall security posture.
Balancing Compliance and Security
While compliance can enhance security, it's essential to avoid implementations that introduce new vulnerabilities. Some compliance measures, if not carefully considered, can create administrative burdens or weaken security in other areas. For example, excessive data retention, if not properly secured, can expand the potential attack surface.
Practical Compliance Strategies
Effective compliance doesn't have to be overly complicated. Some practical strategies include:
-
Documentation: Thoroughly document your security policies, procedures, and compliance efforts. This not only demonstrates compliance but also provides a framework for consistent security practices.
-
Audit Trails: Implement comprehensive audit trails for email access and activity. This helps provide evidence of compliance and assists in incident response.
-
Data Retention: Develop clear data retention policies that meet regulatory requirements while minimizing the amount of sensitive data stored long-term.
Staying Ahead of Emerging Regulations
The regulatory environment is constantly changing. Maintaining long-term compliance and security requires staying informed about emerging privacy regulations and adapting your secure email server strategy. Platforms like Typewire prioritize compliance and security, offering features designed to help organizations meet these evolving requirements. This proactive approach ensures that your email system remains both compliant and secure, regardless of regulatory changes.
Key Takeaways
A secure email server isn't just about sending and receiving emails; it's a critical part of your overall security strategy. This section outlines practical steps to build and maintain a secure email environment, based on real-world examples and expert advice.
Essential Security Practices
These core practices are the foundation of a secure email server:
-
Strong Encryption: Implement robust encryption methods like end-to-end encryption, encryption at rest, and TLS. This protects email content both in transit and when stored on the server, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
-
Robust Authentication: Use strong authentication methods such as two-factor authentication (2FA) and enforce secure password policies. This verifies user identities and makes it much harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
-
Proactive Monitoring: Continuously monitor email traffic for anything suspicious. Use tools like intrusion detection systems, analyze logs, and set up automated alerts. Proactive monitoring helps identify and stop threats quickly.
-
Right Solution: Choose a secure email server solution that fits your organization’s specific needs and technical capabilities. Consider factors like security features, compliance needs, and budget when evaluating both hosted and on-premises options.
Building a Roadmap for Success
Setting up a secure email server requires a strategic approach:
-
Assessment: Start by evaluating your current email security. Find any weaknesses and define your specific security requirements. This sets the stage for a tailored implementation plan.
-
Planning: Create a detailed plan outlining the steps, timelines, and resources needed. This includes choosing the right solution, configuring security settings, and establishing monitoring procedures.
-
Implementation: Execute your plan step by step, focusing on key security measures first. Thorough testing in a controlled environment before going live is essential to mitigate risks.
-
Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly check your secure email server's performance and security. Keep software and security patches updated and adapt your security measures as new threats emerge.
Measuring Success
Don't just assume your email server is secure. Measure its effectiveness with these benchmarks:
-
Reduced Spam and Phishing: A noticeable drop in spam and phishing emails reaching inboxes shows effective filtering and threat detection.
-
Improved Authentication: Higher success rates for legitimate logins and lower rates for unauthorized attempts indicate strong authentication.
-
Faster Incident Response: A fast response to security incidents demonstrates effective monitoring and automated response systems.
-
Compliance Adherence: Ensure compliance with relevant regulations through documentation, audit trails, and proper data retention policies.
Warning Signs and Mitigation
Watch for these red flags and address them promptly:
-
Increased Spam: A sudden rise in spam could indicate a problem with your filters or a new spam campaign. Review and update your spam filter settings.
-
Suspicious Logins: A surge in failed logins may point to brute-force attacks. Strengthen authentication, implement account lockouts, and investigate the source.
-
Unexplained Errors: Investigate unusual system errors or performance issues, as they could be signs of a security breach or technical problems.
Maintaining Long-Term Security
Email server security is an ongoing effort:
-
Regular Audits: Regular security audits help assess your controls and identify any vulnerabilities that need attention.
-
Stay Informed: Keep up with the latest threats and best practices to inform your defenses and security strategies.
-
User Training: Educate users about best practices, including how to spot and avoid phishing attacks and other email threats.
By following these strategies and adapting to the changing threat landscape, you can ensure your secure email server remains a reliable platform for your communications.
Ready to experience secure and private email hosting? Start your free 7-day trial with Typewire today! Get started with Typewire now
Secure Email Server Guide: Build Bulletproof Email Systems
Posted: 2025-06-08
Professional Email Addresses: Your First Line of Defense for Trust and Security
Posted: 2026-02-21
How Do I Block Gmail and Reclaim Your Inbox Privacy
Posted: 2026-02-17
7 Top Canadian Tech Companies Leading in Privacy and Security for 2026
Posted: 2026-02-13
Professional Email Greeting: Master the professional email greeting today
Posted: 2026-02-10
What is Email Phishing: Securing Your Inbox Against Digital Fraud
Posted: 2026-02-06
10 Email Retention Policy Best Practices for Security and Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-02-03
Top 12 Secure Alternatives to Gmail for Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-01-31
What Is Email Alias: A Guide to Better Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-27