Encrypt and Share Files Like a Pro: Your Complete Guide

Why Your Files Need Bulletproof Protection Right Now
In our interconnected world, data breaches are a constant threat. Cybercriminals are using increasingly sophisticated tactics to target vulnerable data. This means encrypting and sharing files is no longer optional, but a necessity for both individuals and businesses. The repercussions of a data breach go far beyond financial losses, impacting reputation, business operations, and even legal compliance.
The Real Cost of Data Breaches
The true cost of a data breach is complex. The financial implications are significant, including recovery expenses, legal fees, and potential fines. However, the damage to an organization's reputation can be even more severe. Lost customer trust and brand erosion can have long-lasting consequences. Operational disruptions from a breach can also cause substantial productivity losses and hinder growth.
The Rise of Encryption as a Necessity
The demand for file encryption software is rapidly increasing. In 2023, the global market was valued at USD 3.7 billion. Projections show it reaching USD 11.6 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 12.1% between 2025 and 2033. This growth reflects the increasing awareness of encryption's vital role in protecting sensitive data. Learn more about the growing market for file encryption software here. Furthermore, regulatory bodies are increasingly requiring encryption across various industries, highlighting its importance for data security.
Emerging Threats and the Need for Advanced Protection
Traditional security measures are often not enough to defend against today's advanced cyber threats. New technologies, such as AI-powered attacks, present challenges that demand sophisticated security solutions. Encryption serves as a vital defense, protecting sensitive data even if other security measures fail. It's like a digital vault, safeguarding your valuable information. This strong protection is essential in a world of ever-evolving threats.
Encryption: Your First Line of Defense
Encrypting and sharing files offers essential protection against data breaches. By converting sensitive data into an unreadable format, encryption ensures that even if a breach occurs, the information remains inaccessible to unauthorized parties. This proactive security approach minimizes potential damage and disruption from cyberattacks. Encryption is a fundamental part of a comprehensive security strategy.
Encryption Basics That Actually Make Sense

Protecting your files begins with a solid understanding of encryption. Imagine sending information two ways: on a postcard, open for anyone to read, or in a sealed envelope, protected from prying eyes. Encryption effectively transforms your data from that exposed postcard into a secure, sealed letter, rendering it unreadable without the proper key.
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Encryption: Two Different Approaches
There are two primary types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses a single key for both encryption and decryption, much like using the same key to lock and unlock a door. This method is generally faster and more efficient, making it well-suited for securing large files. Asymmetric encryption, however, uses two separate keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Think of this like a mailbox: anyone can drop a letter in (encrypt with the public key), but only the mailbox owner has the key to retrieve the contents (decrypt with the private key). For a deeper dive into email encryption, check out this resource: How to master HIPAA compliant email encryption.
AES-256 Encryption: The Industry Standard
The current gold standard for file encryption is AES-256, or Advanced Encryption Standard with a 256-bit key. Its robust security stems from the sheer number of possible key combinations. The odds of cracking AES-256 are astronomically small – comparable to finding a single, specific grain of sand among all the beaches on Earth. This makes it a highly secure choice for protecting sensitive information.
Encryption Keys: Safeguarding Your Data
Encryption keys are the digital codes that lock and unlock your encrypted data. Key length is directly related to security: the longer the key, the stronger the protection. 256-bit keys, like those used in AES-256, offer exceptionally high levels of security. Remember, losing your encryption key is akin to losing the key to a safe – your encrypted data will become inaccessible. Safeguarding your keys is paramount to maintaining data security.
Choosing the Right Encryption Method
The best encryption method for your needs depends on your specific situation. Symmetric encryption's speed makes it a practical choice for sharing files within a controlled environment, like within a company. Asymmetric encryption offers stronger security for sharing information with external parties, ensuring that only the intended recipient can decrypt the data. Understanding these differences allows you to make informed decisions about protecting your files during sharing and storage. Choosing wisely empowers you to establish the right level of security for your individual circumstances.
Finding Your Perfect Encryption Toolkit
Navigating the world of encryption tools can feel overwhelming. From simple file protection to complex enterprise solutions, how do you choose the right tools to encrypt and share files securely? This section provides clarity, helping you find the perfect encryption toolkit for your individual needs.
Evaluating Your Needs and Resources
Before exploring specific tools, assess your requirements. What types of files will you encrypt? How sensitive is the data? Who will you be sharing these files with? Your budget and technical expertise also factor into the decision. A user-friendly application might suffice for a small business owner. However, a large enterprise handling sensitive data will require a more robust, enterprise-grade platform.
Built-In vs. Third-Party Tools
Most operating systems offer basic encryption features like BitLocker for Windows and FileVault for macOS. These are suitable starting points for local file protection. However, they often lack the advanced features of dedicated third-party tools. Third-party solutions offer features like secure file sharing, granular access controls, and stronger encryption algorithms. These additions make them an attractive option for enhanced security and sharing capabilities.
Free vs. Premium: Balancing Cost and Features
Several free encryption tools provide surprisingly robust security, rivaling premium solutions in encryption strength. However, free tools may lack features like secure file sharing, technical support, or advanced access controls. Premium tools frequently include these crucial additions, representing a valuable investment for organizations prioritizing comprehensive security. The choice between free and premium depends on your specific needs and budget.
Cloud-Based vs. Local Encryption: Weighing the Trade-Offs
Cloud-based encryption offers the convenience of accessing your files from anywhere. However, it introduces a potential vulnerability: your data resides on third-party servers. Local encryption, where files are encrypted and stored on your own devices, gives you greater control but limits accessibility. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for selecting the best encryption approach.
Choosing the Right Algorithm: AES vs. PGP
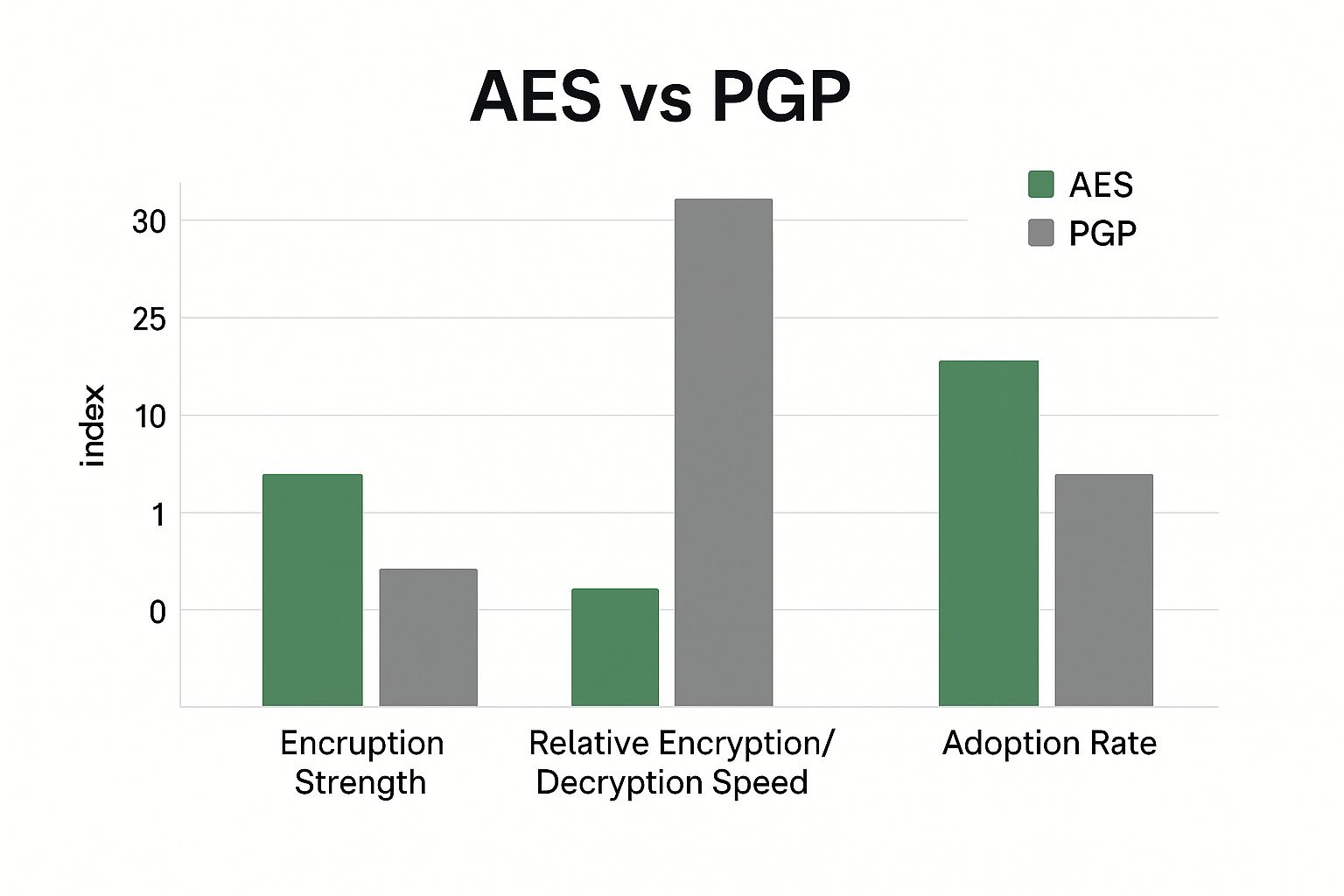
The infographic above compares AES and PGP encryption algorithms. AES generally provides a good balance of speed and security, leading to wider adoption. PGP, although strong, can be slower. This difference makes AES suitable for most general uses, while PGP might be preferred for situations demanding maximum security where speed is less critical.
To help you choose the right tool, let's compare some popular encryption solutions:
The following table provides a head-to-head comparison of leading encryption solutions, highlighting their key features, supported platforms, encryption standards used, and pricing structures. This information will allow you to evaluate the available options and select the best fit for your specific encryption needs.
Top Encryption Tools: Features and Performance
| Tool Name | Encryption Standard | Platform Support | Key Features | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VeraCrypt | AES, Serpent, Twofish | Windows, macOS, Linux | Full-disk encryption, file container creation | Free |
| BitLocker | AES | Windows | Full-disk encryption, device encryption | Included with Windows Pro/Enterprise |
| FileVault | XTS-AES-128 | macOS | Full-disk encryption | Included with macOS |
| AxCrypt | AES-256 | Windows, macOS, iOS, Android | File encryption, cloud storage integration | Free/Premium |
| 7-Zip | AES-256 | Windows, Linux, macOS | File compression and encryption | Free |
As you can see, different tools offer various levels of security, features, and platform compatibility. Consider your needs and resources when making your choice.
Implementation and Ongoing Management
Implementing encryption might seem daunting, but it doesn't have to be. Start small, encrypting a subset of your most sensitive data. Gradually expand your efforts as you gain confidence. Ongoing management is vital. Regularly update your software, back up your encryption keys, and train your team on best practices.
Sharing Encrypted Files Without the Headaches

Encrypting files is essential, but sharing them securely can be tricky. This section explores the challenges of sharing encrypted files and offers practical solutions for various situations.
Key Management: The Cornerstone of Secure Sharing
A solid key management strategy is fundamental to secure file sharing. Your encryption key is like the combination to a safe. Sharing it directly compromises security. Asymmetric encryption offers a better approach. Encrypting a file with the recipient's public key ensures only their private key can decrypt it.
Secure Password Distribution: Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Even with asymmetric encryption, you might need to share passwords for encrypted archives. Sending these through regular email or messaging apps is risky. For more secure email practices, check out this guide: How to Send Email Securely: Your Complete Protection Guide. Using a secure password manager like LastPass or a dedicated secure messaging platform with end-to-end encryption, such as Signal, adds an extra layer of protection.
Collaboration and Access Control: Streamlining Secure Workflows
Team file sharing requires clear protocols. Establish a standard encryption method and key management system. Access controls are crucial for managing who can view, edit, or download files. Cloud storage services often provide features for controlling shared file permissions, ensuring only authorized team members access specific documents. For example, a shared encrypted folder with tiered permissions can manage access effectively.
Troubleshooting Common Sharing Scenarios: Maintaining Control
Problems like lost private keys, forgotten passwords, or software compatibility issues can disrupt sharing. Establish clear procedures for addressing these situations. Key recovery mechanisms, readily available technical support, and up-to-date documentation on encryption and sharing processes are crucial for minimizing disruptions and maintaining data accessibility.
Balancing Security and Usability: Practical Strategies for Success
Security shouldn't come at the cost of usability. If the system is too complex, people won't use it. Choose tools and methods that integrate smoothly into your workflow. Automating tasks like encryption and key management can improve efficiency. Regularly review and adjust your processes to strike the right balance between security and usability, encouraging consistent use and protecting your valuable data.
Industry Trends Shaping File Encryption's Future
The file encryption landscape is in constant flux, influenced by emerging technologies and evolving security needs. Understanding these trends is essential for making smart decisions about encrypting and sharing files effectively, both now and for the future.
The Impact of Remote Work and Cloud Adoption
The increase in remote work and the adoption of cloud computing have significantly amplified the need for robust file encryption solutions. With data continuously moving across networks and stored on remote servers, ensuring its security through encryption is paramount. This shift has driven demand for user-friendly, cloud-based encryption tools that enable secure access and collaboration from anywhere.
Evolving Compliance Requirements: A Driving Force
Regulatory bodies are increasingly requiring stronger data protection measures, including file encryption, across various industries. This trend compels organizations to adopt more robust encryption practices and invest in solutions that comply with these evolving standards. Staying informed about these regulations is crucial for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties.
The Role of AI in Encryption
Artificial intelligence is playing a growing role in shaping the future of file encryption. AI can be used to develop stronger encryption algorithms, automate key management processes, and identify potential vulnerabilities. However, the use of AI in encryption also raises important questions about data privacy and access. Balancing AI's potential with the need to safeguard sensitive information is a key challenge going forward.
Zero Trust Security and File Sharing
Zero trust security models, based on the principle of "never trust, always verify," are influencing how organizations approach file sharing. By requiring authentication and authorization for every access attempt, regardless of location or device, zero trust enhances security for shared encrypted files. This approach highlights the importance of strong encryption and robust access controls to minimize data breaches.
Quantum Computing: A Looming Threat?
The arrival of quantum computing presents a potential threat to current encryption standards. Quantum computers’ immense processing power could break existing encryption algorithms, potentially exposing encrypted data. This has spurred research into quantum-resistant cryptography, designed to withstand attacks from these powerful machines. This emerging field is critical for ensuring the long-term security of encrypted files.
Market Growth and Importance
The encryption software market is experiencing significant growth. In 2024, the market was valued at approximately USD 13.45 billion, and projections suggest it will reach USD 15.29 billion in 2025, representing a CAGR of 13.7%. You can find more detailed statistics here. This growth underscores the increasing importance of encryption in protecting sensitive information.
Preparing for the Future of Encryption
Staying ahead of these trends requires constant vigilance. Businesses and individuals must prioritize investing in up-to-date encryption solutions, implementing strong key management practices, and staying informed about emerging threats and technologies. By proactively approaching file encryption, you can protect your valuable data in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
Advanced Strategies for Specialized Industries

Protecting sensitive data is paramount for every industry. However, sectors like healthcare, finance, legal, and technology face unique data security challenges. These demand advanced encryption and file-sharing solutions that go beyond the basics.
Healthcare: Protecting Patient Data
Healthcare organizations manage highly sensitive patient data. Robust encryption is crucial for complying with regulations like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). This extends beyond encrypting static files. Securely sharing patient information between providers requires stringent access controls and comprehensive audit trails.
End-to-end encryption for telehealth consultations, for example, ensures confidentiality. Automated key rotation further enhances security. This process regularly changes encryption keys, making it significantly harder for attackers to access data, even if a key is compromised.
Finance: Securing Transaction Records
Financial institutions handle massive amounts of sensitive transaction data. Strong encryption is essential to prevent fraud and maintain customer trust. Advanced techniques like time-stamped encryption provide an irrefutable record of data access and encryption times.
This adds an extra layer of security and accountability for financial transactions. Integrating encryption with existing security infrastructure is also crucial for seamless data protection.
Legal: Safeguarding Confidential Documents
Law firms manage confidential client information and legal documents requiring strict confidentiality. Securely encrypting and sharing files is vital for upholding attorney-client privilege. Digital signatures, a critical component of advanced encryption, verify the authenticity and integrity of legal documents, ensuring they remain untampered with during transfer. This protection is essential for legal proceedings and maintaining client trust. The broader data encryption market, encompassing file encryption, is rapidly expanding. In 2024, the market size was approximately USD 18.08 billion. Projections indicate it will reach USD 20.72 billion in 2025, with a CAGR of 14.6%. More detailed statistics are available here.
Technology: Protecting Intellectual Property
Technology companies often possess valuable intellectual property, including source code, proprietary algorithms, and product designs. Securely encrypting and sharing these files, both internally and with partners, is crucial for protecting competitive advantages.
Policy-based encryption rules allow for automatic file encryption based on classification. This ensures sensitive information is always protected. This automated approach simplifies security management and reduces the risk of human error.
Scaling and Integrating Encryption Solutions
Scaling encryption across global teams presents significant challenges. Centralized key management systems and robust access controls are essential for maintaining security and control. Integrating encryption with existing security tools and workflows streamlines implementation and minimizes disruptions, ensuring data protection without impacting productivity.
Lessons Learned from Successful Deployments
Successful encryption deployments often involve a phased approach. This starts with the most sensitive data and gradually expands coverage. Thorough employee training on encryption best practices is also crucial. Regularly reviewing and updating encryption policies ensures they remain effective against evolving threats. This creates a robust and adaptable security strategy.
Your Roadmap to Encryption Success
Successfully encrypting and sharing files requires a well-defined plan. Just as an architect wouldn't begin construction without blueprints, a robust encryption strategy demands a structured approach. This includes outlining clear steps, realistic timelines, and necessary resources.
Planning Your Encryption Rollout
The first step involves identifying which files need encryption. Prioritize sensitive data, such as financial records or personal identification documents. Next, determine the appropriate encryption methods and tools based on your specific needs and technical expertise. For further insight, explore the Top Benefits of Encrypted Email You Need to Know. This careful planning forms the foundation of your encryption strategy.
Implementation and Training
After selecting your encryption tools, implement them gradually. Begin with a small set of files and users to test the process and identify potential issues. Thorough training for all users is essential. Provide clear instructions and helpful resources to ensure everyone understands how to use the chosen encryption tools effectively.
Ongoing Maintenance and Improvement
Encryption is not a one-time task. Ongoing maintenance, such as regular software updates and key backups, is crucial for long-term security. Regularly review your encryption practices and adapt them to emerging threats and evolving needs. This proactive approach, similar to regular car maintenance, prevents major security problems down the line.
Measuring Encryption Effectiveness
How can you determine if your encryption strategy is successful? Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track its effectiveness. These could include metrics like a reduction in security incidents or an increase in user adoption rates. Monitoring these KPIs provides valuable insights into the success of your encryption efforts.
To illustrate a typical encryption rollout, let's look at a sample implementation roadmap. The table below outlines the phases, their duration, key activities, success metrics, and common challenges.
| Phase | Duration | Key Activities | Success Metrics | Common Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | 1 Month | Identify sensitive data, evaluate current security, choose encryption methods | Completion of data inventory, selection of encryption tools | Resistance to change, lack of resources |
| Implementation | 2 Months | Deploy encryption tools, configure settings, test functionality | Successful encryption of target files, user training completion | Technical difficulties, user adoption |
| Training | 1 Month | Conduct user training, provide documentation, establish support channels | User proficiency with encryption tools, positive user feedback | Lack of engagement, understanding complexities |
| Monitoring & Review | Ongoing | Monitor KPIs, update software, adapt to new threats | Improved security posture, reduced security incidents | Maintaining user vigilance, staying updated on threats |
This table demonstrates how a phased approach allows for focused efforts and measurable progress at each stage. By tracking success metrics, you can identify areas for improvement and ensure the ongoing effectiveness of your encryption strategy.
Ready for secure and seamless email communication? Start your free trial with Typewire today!
Encrypt and Share Files Like a Pro: Your Complete Guide
Posted: 2025-06-04
Top 12 Secure Alternatives to Gmail for Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-01-31
What Is Email Alias: A Guide to Better Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-27
How to Send an Encrypted Email and Protect Your Digital Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-23
Email Hosting Canada The Definitive Guide to Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-01-20
How to Send Email Securely: A Guide to Real Privacy & Security
Posted: 2026-01-16
Why Am I Getting So Many Junk Emails? A Guide to Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-13
How to Disable Email Tracking and Protect Your Email Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-09
Secure Email Services: A Guide to True Email Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-01-06