How to Send a Secure Email in Gmail

Sending a secure email in Gmail is easier than you might think. You can jump right in with the built-in Confidential Mode to add expiration dates and block forwarding, or if you're on a Google Workspace account, you can step up to full S/MIME encryption. These features are your go-to tools for turning a regular email into a protected message, adding critical layers of security when you're handling sensitive information. Getting comfortable with them is the key to keeping your private communications private.
Why Securing Your Gmail Is a Non-Negotiable Skill

Think about what's sitting in your inbox right now. It's more than just a place to chat; it's a digital vault. You've got bank statements, signed contracts, private conversations, and maybe even strategic business plans all in one place. Leaving the security of those messages to chance is a massive gamble in a world where data breaches are front-page news.
An unencrypted email is often described as a postcard. As it makes its way across the internet, anyone along the route can potentially read its contents. This vulnerability means your most sensitive information is out in the open, making robust security measures an absolute must-have for modern communication, not just a "nice-to-have."
Understanding Common Email Threats
The threats facing your email are both relentless and creative, ranging from wide-net automated attacks to carefully crafted schemes meant to trick you personally. Knowing what you're up against is the first step toward building a solid defense.
Here are a few of the most common vulnerabilities you should be aware of:
- Interception: Attackers can snatch emails right out of the air as they travel across networks. This is especially risky on public Wi-Fi, where they can read your messages as easily as if they were written on a postcard.
- Phishing Attacks: These are the sneaky emails that look like they're from a trusted source, like your bank or a colleague. Their whole purpose is to trick you into giving up login credentials, financial info, or other personal data.
- Unauthorized Access: If a hacker gets into your account—or your recipient's—they suddenly have access to your entire email history. That's a huge privacy breach waiting to happen.
Phishing attempts are an ever-present danger, so learning solid phishing attack prevention strategies is essential for keeping your Gmail account from being compromised.
A proactive approach to email security is your strongest defense. By learning how to send a secure email in Gmail, you shift from being a potential target to being an informed and protected user.
At the end of the day, the goal is simple: make sure your private messages stay private. The tools and best practices we'll cover are designed to plug these security holes, putting you in control of who sees your information and for how long. This mindset is what turns email from a potential liability into a secure and reliable way to communicate.
Using Gmail Confidential Mode for Everyday Protection
Right inside Gmail, you have a surprisingly powerful tool for protecting sensitive messages: Confidential Mode. It's not hidden away in some complex settings menu; you'll find it by clicking the little lock and clock icon in your compose window.
Think of it as adding a self-destruct timer to your emails. You can set:
- Expiration Dates: Make a message vanish after a day, a week, or a month. No more lingering sensitive data.
- SMS Passcodes: Add a second layer of verification. The recipient can't open the email until they enter a code sent to their phone.
- Action Blocks: This is a big one. It prevents recipients from forwarding, copying, printing, or downloading your message and its attachments.
It's perfect for those everyday situations where you need a bit more control. Imagine sending over a draft of a contract. By setting a one-week expiration, you prevent an old version from floating around in someone’s inbox indefinitely.
Or what about sharing a scan of your passport? That’s not something you want sitting unprotected. Requiring an SMS passcode ensures that even if someone gains access to the recipient's email account, they still can't view that message without also having their phone.
How It Stacks Up
It's important to understand what Confidential Mode does and doesn't do. Gmail already uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt messages while they're in transit and 128-bit encryption when they're sitting on Google's servers.
Confidential Mode adds a layer of access control on top of that. It’s not true end-to-end encryption, which means Google technically still has the ability to access the message content. This is how they power features like spam filtering.
The biggest limitation? It can't stop a determined person from taking a screenshot or a photo of their screen.
Confidential Mode is fantastic for adding friction and protecting against casual sharing or accidental forwarding. It's not a digital vault for state secrets.
When you're setting an expiration date, try to find a sweet spot. A short deadline is great for security but can be a real headache for a busy recipient who misses the window. For passcodes, you can choose between a code sent to their email or an SMS code sent to their phone. The SMS option is definitely more secure, but you have to be sure you have the right mobile number.
| Feature | Protection Level |
|---|---|
| Standard Gmail (TLS) | Encrypted only while traveling between servers |
| Confidential Mode | Adds expiration dates and disables sharing/downloads |
This simple toggle takes your email from a standard postcard to a letter in a sealed envelope with a "return to sender" date stamped on it.

As you can see, activating it is just a click away. You compose your email as usual, hit the icon, and choose your settings before you send.
Ready to give it a try?
- In the compose window, click the lock and clock icon at the bottom.
- Choose your expiration date and whether to require a passcode.
- Click Save, and you're good to go.
If you're looking for even more ways to lock down your messages, you might find our guide on password-protecting emails helpful. You can learn more here: https://typewire.com/blog/read/2025-09-12-how-to-protect-an-email-with-password-simple-and-effective-tips
Best Practices for Confidential Mode
Getting the most out of this feature just takes a little forethought. Here are a few tips I've picked up:
- Write clear subject lines. If an email has a short fuse, give the recipient a heads-up like "Action Required: Contract Review (Expires in 3 days)."
- Double-check mobile numbers. A typo in a phone number for an SMS passcode means your recipient is completely locked out.
- Layer your security. For Google Workspace users, combining Confidential Mode with S/MIME encryption provides a much stronger level of security for truly sensitive corporate data.
Following these simple rules makes the process smoother for everyone and avoids frustrating back-and-forth exchanges.
A Real-World Example
A law firm I know, Blue River Legal, uses Confidential Mode as part of their standard workflow. When attorneys send draft agreements to clients, they set a two-day expiration. This simple step prevents clients from accidentally referencing an outdated version later on and gives them confidence that their sensitive legal documents aren't just sitting in an inbox forever.
It’s a perfect illustration of how to integrate a security feature without bringing in complex, clunky software.
Key Takeaway: Confidential Mode strikes a practical balance between ease of use and enhanced security, making it an excellent tool for everyday confidential communication.
The best way to get comfortable with it is to use it. Try sending a confidential email today and see how easily it fits into your routine.
Choosing the Right Gmail Security Method
Not all sensitive information needs the same level of digital armor. The trick is knowing which of Gmail's security features to use and when, so you can protect your data without making things overly complicated. Think of it this way: you wouldn't use a bank vault for your lunch, but you also wouldn't use a paper bag to protect gold bars.
The same logic applies when you send a secure email in Gmail.
For most of your day-to-day messages, the standard Transport Layer Security (TLS) that Gmail applies automatically is more than enough. It creates a secure tunnel, encrypting your email as it travels from you to the recipient's server, which prevents anyone from snooping on it mid-journey.
But once that email arrives, its safety is in the hands of the recipient's email provider and their account security. This is the point where you have to decide if you need more control over the message itself.
Deciding Your Level of Protection
When you’re sending something more sensitive—say, a business proposal, personal health records, or a client's invoice—it's time to step up your security game. This is where you'll want to look at Confidential Mode or S/MIME encryption, both of which offer very different kinds of control.
- Confidential Mode: This is your best bet for preventing casual sharing. It’s perfect for sending documents you don’t want the recipient to copy, forward, or print. It acts as a powerful deterrent.
- S/MIME Encryption: This is the big gun, reserved for Google Workspace users. S/MIME provides true end-to-end encryption, scrambling the email's content so that only the intended recipient with the right digital key can ever decipher it.
The real-world impact of strong encryption like S/MIME in a business environment is pretty significant, as the data below shows.
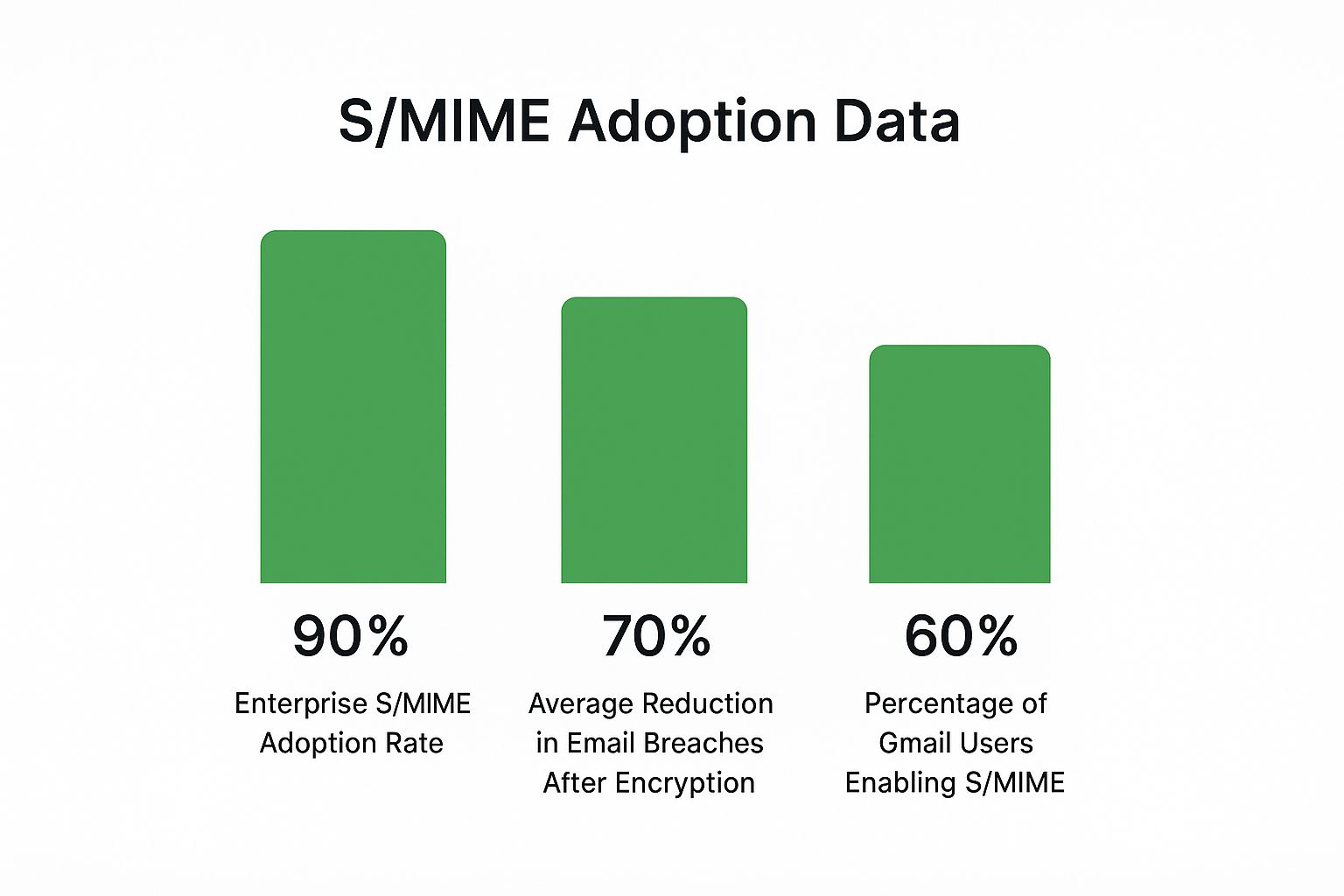
While encryption adoption is already high in many corporate settings, the numbers clearly show it dramatically cuts down on security incidents. Picking the right tool for the job is a critical piece of any solid security strategy.
Gmail Security Methods at a Glance
Making the right call often comes down to understanding the specific situation you're in. I've put together a quick comparison to help you see when each method works best.
The goal is to match the security tool to the sensitivity of the information. Over-encrypting can be cumbersome, but under-protecting can be disastrous.
Here’s a simple breakdown of your options.
| Security Feature | Level of Protection | Best For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard TLS | Basic: Protects email only during transit. | Everyday, non-sensitive communication. | Not protected on the recipient's server. |
| Confidential Mode | Enhanced: Adds access controls like expiration and blocks sharing. | Sending contracts, invoices, or personal data to trusted parties. | Cannot prevent screenshots or photos of the screen. |
| S/MIME | Advanced: End-to-end encryption of the email content. | Transmitting highly sensitive corporate or legal documents. | Requires a Google Workspace account and setup by both parties. |
Ultimately, learning how to send a secure email in Gmail is less about just clicking a button and more about making an informed decision. For sharing family photos, standard TLS is fine. For that draft business plan, Confidential Mode is a smart move. And for those legally binding documents, S/MIME gives you the robust, ironclad protection you really need.
Securing Your Email Attachments Like a Pro
An email is only as secure as its weakest link, and that's almost always an unencrypted attachment. Sending a sensitive document without locking it down first is like mailing a sealed letter but taping the key to the outside of the envelope. Real security means protecting the file itself, long before it ever leaves your computer.
This is non-negotiable for files containing financial records, personal identification, or confidential business plans. The good news is, you probably already have the tools you need. Most modern operating systems have built-in features for creating password-protected files, making it a surprisingly simple process.
Pre-Encrypting Your Files for Maximum Safety
The smartest move you can make is to encrypt your documents locally. I'm talking about creating a password-protected PDF or a compressed ZIP archive. This approach wraps your file in a protective layer that travels with it, completely separate from the security of the email itself.
Let's say you're sending a signed contract. You can save it as a PDF and set a strong password right inside your PDF software. Or, if you have a folder full of financial statements, compressing them into a single, encrypted ZIP file is both efficient and secure. This way, even if someone managed to intercept your email, the attachments would be useless gibberish without the password.
Crucial Pro-Tip: Never, ever send the password in the same email as the attachment. That completely defeats the purpose. Always share the password through a different channel—a quick text message or a phone call works perfectly.
This two-channel approach creates a huge hurdle for any would-be attacker. They would have to compromise both your email and your secondary communication method, which is a much taller order.
Using Google Drive for Superior Control
Sometimes, attaching a file directly isn't the best play, especially with large files or highly sensitive documents. A far better alternative is to upload the file to Google Drive and share a secure link instead. This method gives you incredible control over who can access your file and what they can do with it.
When you share from Google Drive, you can get really specific:
- Restrict Access: You can choose exactly which Google accounts can view, comment on, or edit the file. No one else gets in.
- Set Expiration Dates: Just like with Confidential Mode, you can set a ticking clock on access, which automatically locks the file after a certain period.
- Disable Downloading: This is a big one. You can prevent people from downloading, printing, or even copying the contents of the file.
This strategy turns file sharing from a "fire and forget" action into a managed, controlled process. If you need to cut off access, you can do it instantly from your Google Drive, even well after the email has been sent. Our detailed guide on how to encrypt and share files like a pro dives even deeper into these advanced techniques.
While you're taking these steps, it's comforting to know that Gmail is doing its part in the background. With a 99.9% spam detection rate and Transport Layer Security (TLS) on by default, Google gives you a solid foundation. In fact, studies show that enabling features like two-step verification has helped slash Gmail account breaches by as much as 50%. You can explore Gmail's security statistics and insights for a closer look at the data.
Fortifying Your Core Gmail Account Security
Sending an encrypted email is great, but it won’t stop an attacker who already has the keys to your account. Think of your Gmail credentials as the front door to your digital life. If that door swings open too easily, everything inside—attachments, drafts, contacts—becomes fair game.
The single most effective shield is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA). Imagine your password as one lock on your vault; 2FA adds another. Even if someone snags your password, they’ll hit a brick wall without the one-time code on your phone or your hardware security key.
You can find our in-depth look at this essential layer in a guide to multi-factor authentication email security to see how powerful it is.
Perform A Google Security Checkup
Google’s Security Checkup is like a wellness exam for your account. Schedule it twice a year—or right after any suspicious activity—and spend ten minutes working through its recommendations.
• Connected Apps
Review every third-party app linked to your Gmail. If you aren’t opening that calendar or note-taking tool anymore, revoke its access. Each integration can be an entry point.
• Recent Security Activity
Look for unfamiliar logins and alerts. A sign-in from halfway around the world? That’s a red flag.
• Your Saved Passwords
Google flags any weak, repeated, or compromised passwords you’ve stored. Replace them with stronger alternatives immediately.
Taking ten minutes for a Security Checkup can uncover vulnerabilities you never knew existed. It’s one of the highest-impact security actions you can take.
Mastering Passwords And Spotting Phishing
A robust password does more than hit a character count. It’s a unique phrase, mixer of cases, numbers, and symbols—and it lives only on one site. A password manager automates this process, generating and storing credentials so you don’t have to remember a dozen complex strings.
When it comes to phishing, be your own first line of defense. Pause before you click any link that urges immediate action or account verification. Check the sender address, hover over links to see where they really go, and never enter credentials on a page you didn’t navigate to yourself.
Gmail’s built-in protections are formidable: over 2.5 billion users rely on it every day, and it filters nearly 15 billion spam emails daily. Learn more about Gmail’s robust security features and let your own vigilance fill in the gaps.
Got Questions About Gmail Security? We Have Answers

As you start digging into Gmail’s security features, you're bound to have a few questions. That's perfectly normal. Getting a handle on the specifics is what separates a novice from someone who truly understands how to protect their information.
Let's clear up some of the most common sticking points so you can send emails with confidence.
A big one I hear all the time is about Confidential Mode. Is it actually secure? Well, it's complicated. This feature is fantastic for adding access controls. You can set expiration dates, require SMS passcodes, and block recipients from forwarding, copying, or downloading your message.
But here’s the crucial part: it's not the same thing as end-to-end encryption. Google’s servers can still see and process the content of the message.
Think of Confidential Mode as a strong deterrent against casual sharing, not an unbreakable vault. It's excellent for sending sensitive information to trusted recipients, but it's not designed for state secrets.
And remember, nothing stops someone from simply taking a screenshot or a photo of their screen. Confidential Mode can't prevent that, so always keep that limitation in mind before you hit send.
Making Sense of Encryption Lingo
The terminology around encryption can feel a bit overwhelming, but understanding the two main types you'll run into with Gmail makes a world of difference. They offer very different levels of protection.
- Transport Layer Security (TLS): This is Gmail’s standard, default protection. It basically creates a secure tunnel for your email while it's traveling between servers. This is great for stopping bad actors from snooping on your message in transit, but once it arrives at a server, it's readable.
- End-to-End Encryption (E2EE): This is the next level up, used by more advanced tools like S/MIME. It encrypts the message right on your device, and only the intended recipient has the key to decrypt it. The servers in the middle, including Google's, have no way to read the content. E2EE offers a far superior level of privacy.
How to Tell if an Email is Secure
So, what about the emails you get? How can you tell if the sender took steps to protect the message? Thankfully, Gmail provides a few visual clues.
Most emails sent with standard TLS will have a small padlock icon next to the sender's details. It's a good sign that the basics are covered.
If an email arrives via Confidential Mode, you can't miss it. Gmail displays a large notification at the bottom explaining the restrictions and showing the expiration date.
For messages locked down with S/MIME, you'll typically see a prominent green padlock. This signals a very high, verified level of security. Learning to spot these icons is a quick way to gauge the security of the information you receive.
Ready for an email experience where security isn't an afterthought? Typewire provides private, secure email hosting that puts you back in control. Say goodbye to tracking and data mining, and hello to true communication privacy.
How to Send a Secure Email in Gmail
Posted: 2025-09-22
Professional Email Addresses: Your First Line of Defense for Trust and Security
Posted: 2026-02-21
How Do I Block Gmail and Reclaim Your Inbox Privacy
Posted: 2026-02-17
7 Top Canadian Tech Companies Leading in Privacy and Security for 2026
Posted: 2026-02-13
Professional Email Greeting: Master the professional email greeting today
Posted: 2026-02-10
What is Email Phishing: Securing Your Inbox Against Digital Fraud
Posted: 2026-02-06
10 Email Retention Policy Best Practices for Security and Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-02-03
Top 12 Secure Alternatives to Gmail for Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-01-31
What Is Email Alias: A Guide to Better Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-27