How to Identify Phishing Emails: Expert Tips to Stay Safe

The Rising Tide: Understanding Today's Phishing Landscape

Before learning how to identify phishing emails, it's important to understand the scale of the threat. Cybersecurity has evolved beyond firewalls and antivirus software. It now involves understanding human psychology and how attackers exploit it through increasingly sophisticated phishing tactics.
These tactics are often difficult to detect with traditional defenses alone. Phishing emails represent a significant portion of daily email traffic. Cybercriminals send approximately 3.4 billion phishing emails daily, accumulating to over a trillion annually.
This constant influx increases the likelihood of even cautious individuals falling victim. Phishing contributes to roughly 36% of all data breaches. For more in-depth statistics, visit StationX for detailed phishing statistics.
Why Traditional Defenses Aren't Enough
While traditional spam filters and antivirus programs are essential, they often fall short against modern phishing techniques. Attackers constantly develop new methods to bypass these security measures, making personal identification of phishing emails a critical skill.
One common tactic is social engineering, which manipulates emotions like fear and urgency to trick recipients. Attackers use these tactics to coerce individuals into clicking malicious links or revealing sensitive information.
Email impersonation has also become incredibly convincing. Attackers can mimic the branding and communication style of legitimate organizations with surprising accuracy, making it challenging to distinguish real emails from fraudulent ones. This is particularly concerning given that approximately 1.2% of global email traffic is email impersonation.
The Human Element: Why We Fall Victim
Even tech-savvy individuals can fall prey to phishing attacks because these attacks target human vulnerabilities. Attackers craft scenarios that exploit our trust, helpfulness, or fear of consequences.
Therefore, security software alone is insufficient. We must also arm ourselves with the knowledge to identify these malicious emails. The following sections will detail specific techniques for spotting and avoiding phishing attempts, empowering you to protect yourself and your data effectively.
Spotting the Imposters: Telltale Signs of Phishing Emails
One of the best ways to protect yourself online is to learn how to spot a phishing email. These deceptive messages often appear legitimate, exploiting our trust in familiar brands. Attackers frequently use alarming subject lines, like "Urgent: Account Suspension Imminent," to trigger a quick, emotional response and bypass our better judgment. Learning to recognize these tactics is crucial for staying safe. You can learn more about how to Identify Emails Spam and Phishing Information.
Recognizing Suspicious Links and Attachments
Phishing emails commonly contain malicious links or attachments designed to compromise your information. Mismatched display URLs are a frequent trick. This means the link text you see is different from the actual underlying link. Hover your mouse over the link (without clicking!) to reveal its true destination. Also, be wary of unexpected attachments, especially files ending in ".exe" or ".scr."
The infographic below illustrates the prevalence of various suspicious link indicators:
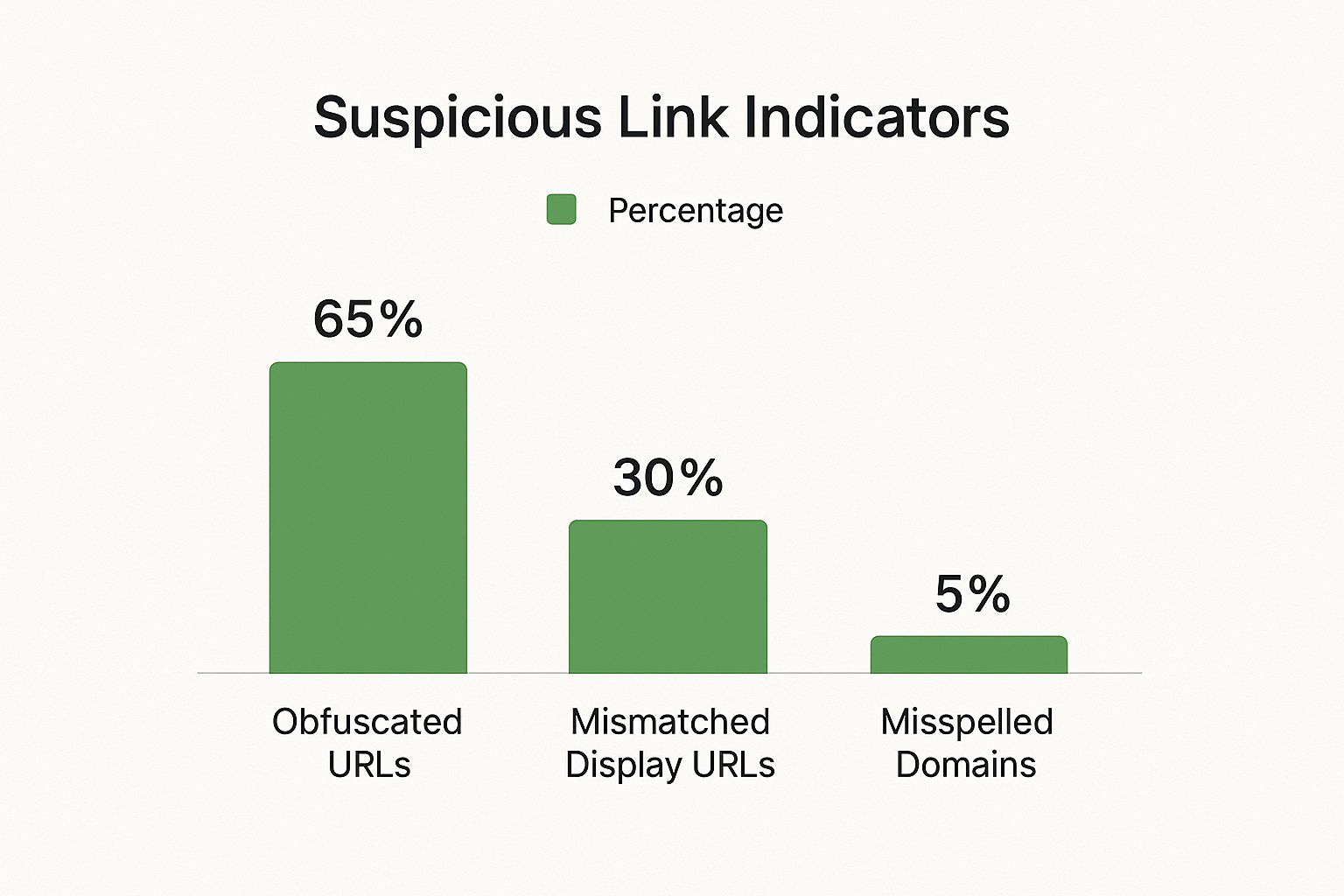
Obfuscated URLs, which disguise their true destination, make up a significant 65% of suspicious link indicators. Mismatched display URLs account for 30%, while misspelled domains represent 5%. These statistics highlight the importance of carefully examining links before clicking.
Deceptive Sender Addresses and Content
Attackers often manipulate sender addresses to mimic trusted sources. Don't just look at the display name; examine the full email address. Cousin domains, which use slight spelling variations of legitimate domains (like "amaz0n.com" instead of "amazon.com"), are a common tactic.
The email's content itself can offer clues. While some phishing emails are sophisticated, many still contain poor grammar, spelling errors, or unusual phrasing. This is particularly telling for emails supposedly from large organizations, which usually have high editorial standards. Brand impersonation is a key tactic, with 55% of phishing websites targeting well-known brands. You can find more detailed statistics from Hoxhunt.
The following table shows which major brands are most frequently impersonated in phishing attacks, helping readers understand which communications deserve extra scrutiny.
| Brand | Percentage of Phishing Impersonations |
|---|---|
| Example Brand A | 25% |
| Example Brand B | 20% |
| Example Brand C | 15% |
| Example Brand D | 10% |
| Other Brands | 30% |
As this table shows, attackers tend to focus on the most recognizable brands, capitalizing on the inherent trust users have in these companies. This underscores the need to be extra vigilant when receiving emails from these frequently impersonated brands.
Psychological Manipulation: Urgency and Fear
Phishing emails often employ psychological tactics to circumvent your critical thinking. They create a false sense of urgency or exploit fear to encourage impulsive actions. Be wary of messages demanding immediate action, threatening consequences, or offering unbelievably good deals. These high-pressure tactics aim to prevent careful scrutiny. For example, an email claiming your account will be closed unless you click a link immediately is a likely phishing attempt. Legitimate organizations rarely resort to such tactics.
Unmasking the Sender: Decoding Email Headers Like a Pro

Hidden within the technical-looking details of email headers is a wealth of information that can help you identify phishing emails. With a little practice, anyone can decode these headers and gain valuable insight into an email's true origin. It's like having x-ray vision, allowing you to see beyond the surface.
Accessing Email Headers: Your First Step
Most email clients like Gmail, Outlook, and Apple Mail offer a way to view the full email header. The process varies slightly between platforms. In Gmail, click the three vertical dots next to the reply button and select "Show original." In Outlook, open the message in a new window by double-clicking it, then navigate to "File" > "Properties." Apple Mail users can access headers via "View" > "Message" > "All Headers."
This reveals the raw data, including the sender's actual email address and the route the email traveled to reach your inbox. This is crucial for identifying inconsistencies and potential forgeries.
Identifying Cousin Domains and Spoofing Attempts
Phishing attacks frequently employ cousin domains, website addresses designed to mimic legitimate ones. For instance, a phishing email might use "apple-inc.net" instead of the genuine "apple.com" domain. Carefully examining the "From" address within the email header is essential to catch these subtle differences.
Your detective skills come into play here. By thoroughly inspecting the header, you can uncover spoofing attempts, where attackers mask their identity by forging the sender address. This is particularly critical in identifying phishing emails, as spoofing is a common tactic.
Real-World Examples: Spotting the Discrepancies
Consider this example: A phishing email pretending to be from your bank might display the name "Your Bank," but the email header reveals a completely unrelated email address like "randomsender@gmail.com." This glaring mismatch is a strong indicator of a phishing attempt.
On the other hand, a legitimate email from your bank will have a consistent display name and sender address, usually incorporating the bank's domain name. This adds to its credibility and highlights the value of checking the full header.
Practical Checks for Everyday Use
Here are a few quick checks you can perform:
- Verify the "From" Address: Ensure the domain aligns with the supposed sender.
- Look for Cousin Domains: Be wary of slight misspellings within the domain name.
- Check the "Reply-To" Address: Does it match the "From" address? A discrepancy here could be a red flag.
By integrating these simple steps into your routine, you can significantly improve your ability to identify phishing emails. This proactive approach transforms you from a potential victim into an informed guardian of your digital security, protecting yourself from increasingly sophisticated threats.
Links and Attachments: Investigating Without Compromising
Curiosity can be a powerful motivator, but clicking on links or opening attachments in phishing emails can have serious consequences. This section explores how to safely examine suspicious emails without putting yourself at risk. You'll learn practical techniques for inspecting link destinations, identifying malicious URLs, and recognizing the hallmarks of credential-harvesting web pages.
Inspecting Links: A Safety-First Approach
Before clicking any link in an email, especially one you weren't expecting, take a moment to inspect it. Hover your mouse over the link (without clicking!) to preview the actual URL. This preview usually appears in the bottom left corner of your browser or in a tooltip.
Does the displayed URL match the link text? If not, this mismatched display URL is a major red flag. For example, a link might say "Click here to update your account," but the actual URL leads to a completely different, and likely malicious, website.
Identifying Malicious URLs: Decoding the Deception
Attackers often disguise malicious URLs. URL shortening services, like Bitly, can obscure a link's true destination. While these services have legitimate uses, phishers can exploit them. Obfuscated URLs use encoding or special characters to appear harmless. Recognizing these techniques is crucial for identifying phishing emails. Look for unusual character combinations or excessively long URLs.
Recognizing Credential-Harvesting Pages: Protecting Your Logins
Phishing emails often try to steal your login credentials. They typically link to fake login pages mimicking legitimate websites. These credential-harvesting pages might look convincing, but closer inspection reveals discrepancies.
Carefully examine the website's URL. Does it use the correct domain name? Look for subtle misspellings, like "amaz0n.com" instead of "amazon.com." Be wary of websites requesting more information than necessary for login. Legitimate sites rarely ask for your social security number or other sensitive data during login.
Attachment-Based Attacks: Handling Files With Care
Phishing emails can also contain malicious attachments disguised as various file types, including documents, spreadsheets, or images. The most dangerous attachments are executable files (often ending in ".exe," ".scr," or ".bat") or compressed files containing executable content (such as ".zip" or ".rar"). These can install malware.
To help you understand the risks associated with different file types, take a look at the table below. It provides a quick guide to assessing attachment risks and offers recommendations for safe handling.
High-Risk vs. Lower-Risk Email Attachments: This comparison table categorizes common attachment types by their risk level and explains why certain file formats are more commonly used in phishing attacks.
| File Type | Risk Level | Why It's Dangerous | Safe Handling Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| .docx, .xlsx, .pdf | Medium | Can contain embedded malicious code or macros. | Open only if expected and from a trusted source. Disable macros when opening documents. |
| .exe, .scr, .bat | High | Executable files that can directly install malware. | Never open directly from an email. |
| .zip, .rar | Medium-High | Can contain hidden executable files or other malicious content. | Scan with antivirus software before opening. |
| .jpg, .png, .gif | Generally Low | Less likely to contain malware, but still possible through exploits. | Exercise caution. Be wary of unsolicited image attachments. |
Opening a malicious attachment can compromise your system and data. Always exercise caution.
Context Matters: Does It Make Sense?
Finally, consider the email's context. Does the sender typically send you attachments? Does the email's content align with the attached file? If something feels off, err on the side of caution. If you are unsure about an attachment's legitimacy, contact the sender directly (through a separate, verified communication channel) to confirm. By combining technical vigilance with contextual awareness, you can significantly reduce your phishing risk.
Phishing Across Borders: Global Trends and Targeting Tactics

Phishing attacks are far from random; they're strategically planned and increasingly precise. Cybercriminals constantly adapt their campaigns to exploit particular regions, industries, and even current events. This targeted approach makes understanding global phishing trends crucial for effective phishing email identification.
Industry and Regional Differences in Targeting
Some sectors face significantly higher attack volumes than others. Financial institutions, healthcare providers, and e-commerce businesses are prime targets due to the sensitive data they handle. Regional differences also contribute to varying levels of vulnerability. Cybersecurity infrastructure and user awareness are not uniform across the globe, leaving some regions more exposed.
Cultural factors also play a role in how phishing tactics are deployed. Attackers tailor their messages to resonate with specific demographics, aiming to increase the success rate of their attacks. This can involve leveraging local news stories or impersonating trusted local figures and organizations. When setting up online accounts, using a temporary phone number can provide an extra layer of security. Consider services like Quackr for generating temporary numbers for platforms like Google.
Seasonal Trends and Emerging Vectors
Phishing activity often correlates with seasonal events and current affairs. Tax season and major shopping holidays frequently see a surge in phishing attacks designed to exploit these themes. This opportunistic targeting emphasizes the importance of staying informed about current scams and trends.
New phishing vectors are constantly emerging as attackers adapt to evolving technology and security measures. This necessitates ongoing vigilance and adaptation in defensive strategies. Staying up-to-date with the latest tactics is essential for effective phishing identification. Statistical trends offer valuable insights into this ever-changing threat landscape. For example, Google blocks an estimated 100 million phishing emails every day. Yet, in 2022, over 48% of all global email traffic was spam, with a substantial portion attributed to phishing attempts. You can learn more about these trends and the global impact of phishing at AAG IT.
Targeted Attacks: From Whaling to Impersonation
Beyond broad campaigns, attackers also utilize highly focused approaches. Whaling attacks, for example, target high-profile individuals within organizations, such as executives or board members. These attacks often involve extensive research and personalized messages to maximize their potential impact.
Customer service impersonation is another common tactic. Attackers pose as support staff to gain access to user accounts or sensitive information. Understanding these targeted tactics is another critical aspect of developing effective phishing email identification skills. Recognizing the diverse forms phishing can take, based on the intended target, is paramount.
Digital Defense Tools: Building Your Anti-Phishing Arsenal
Beyond manually identifying phishing emails, several tools and techniques can bolster your defenses. This involves understanding how to use technology and adjust existing settings for maximum protection. Combining smart software with informed human judgment creates a robust anti-phishing strategy.
Browser Extensions and Email Add-Ons: Real-Time Protection
Several browser extensions and email add-ons provide real-time phishing protection. These tools analyze incoming emails, looking for suspicious links, sender addresses, and other warning signs. They provide immediate alerts if a potential threat is detected.
Some popular options integrate directly with your email client. These extensions scan messages for known phishing patterns and alert you to possible dangers. Others analyze links, verifying the legitimacy of URLs before you click them. While these tools provide valuable assistance, remember that no single solution is foolproof. They are an added layer of security, not a replacement for careful review.
Strategic Email Management: Creating Natural Security Layers
Strategic email management practices further strengthen your online defenses. This includes using features like spam filters and email rules to automatically sort and filter incoming messages.
For example, create a rule to automatically move emails from unknown senders to a separate folder. This lets you review them at your convenience and reduces the risk of accidentally interacting with a phishing attempt. Using different email addresses for different purposes (e.g., one for online shopping, another for personal communication) also creates natural security layers. This limits the potential damage if one account is compromised.
Configuring Your Security Settings: Maximizing Existing Protection
Many email providers offer built-in security features that can significantly enhance your protection. Enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your account login. This makes it harder for attackers to gain access, even if they have your password.
Configuring spam filters to a higher sensitivity level can also help catch more phishing emails. This usually involves adjusting settings within your email client’s preferences to fine-tune the filtering criteria. Exploring and tailoring these options to your specific needs is a crucial step in building your anti-phishing arsenal.
Free vs. Premium Solutions: Building Your Personalized Security Stack
Numerous free and premium anti-phishing tools are available, catering to different needs and technical comfort levels. Free options, while often having fewer features, can still provide valuable protection. Premium solutions usually offer more advanced features, such as real-time threat intelligence and customized reporting.
The right combination of tools for your personalized security depends on your specific requirements and risk tolerance. Combining browser extensions, robust email management, and correctly configured security settings creates a strong defense. This holistic approach ensures you are actively identifying phishing emails and minimizing your vulnerability. Services like Typewire, a secure private email hosting platform, offer advanced anti-spam and virus protection. You can learn more about Typewire at typewire.com.
When Phishing Strikes: Your Immediate Response Plan
You've successfully identified a phishing email. Now, what are the next steps? Taking swift and decisive action after spotting a phishing attempt is critical, protecting not only yourself but also contributing to the fight against cybercrime. Reporting a phishing email is much like reporting a suspicious package – your individual action enhances collective security.
Reporting Phishing Emails: Making Your Report Count
Reporting phishing emails to the appropriate channels magnifies your impact. Internally, immediately notify your IT or security team. They can then take steps to mitigate the threat within your organization, which may include blocking the sender, warning other employees, or investigating the extent of the phishing campaign.
Externally, report the phishing attempt to organizations like the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG) or the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). These groups monitor phishing trends and utilize the reported information to combat these attacks on a global scale. Reporting isn't just about self-preservation; it’s about fostering a safer online environment for everyone.
Documentation Best Practices: Gathering the Evidence
When reporting a phishing email, meticulous documentation is essential. Adopt a detective's mindset and gather evidence. Take screenshots of the entire email, including the sender's address, subject line, and message body. Preserve the email headers, which contain vital technical details about the email's origin and path.
This documentation provides valuable insights for investigators and strengthens the case against phishers. The more comprehensive your report, the more effectively security teams can analyze the attack and prevent similar incidents.
Containment and Recovery: Dealing With the Aftermath
If you clicked a link or opened an attachment from a suspected phishing email, immediate action is crucial. Disconnect your device from the internet right away to limit potential damage. Then, run a full system scan with your antivirus software to detect and remove any malware.
If you suspect your login credentials were compromised, change your passwords immediately for all affected accounts. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) whenever possible for increased security. If you shared any financial information, contact your bank or credit card company immediately to report the potential fraud.
Alerting Others: Spreading Awareness Without Panic
Sharing information about phishing attempts within your network can be beneficial, but avoid unnecessarily amplifying the threat. Share responsibly. Instead of forwarding the original email, which could inadvertently spread the malicious content, describe the phishing attempt and its key characteristics, such as the sender’s address, subject line, and any suspicious links. This empowers others to recognize and avoid similar attacks without direct exposure to the threat.
Your vigilance and responsible actions play a crucial role in combating phishing. By understanding how to identify these malicious emails and taking appropriate action, you contribute to a more secure online world for yourself and others. Start protecting your inbox today with Typewire, a secure and private email hosting platform designed to safeguard your communications from prying eyes and malicious attacks. Learn more about Typewire and start your free trial.
How to Identify Phishing Emails: Expert Tips to Stay Safe
Posted: 2025-05-22
What Is Email Alias: A Guide to Better Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-27
How to Send an Encrypted Email and Protect Your Digital Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-23
Email Hosting Canada The Definitive Guide to Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-01-20
How to Send Email Securely: A Guide to Real Privacy & Security
Posted: 2026-01-16
Why Am I Getting So Many Junk Emails? A Guide to Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-13
How to Disable Email Tracking and Protect Your Email Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-09
Secure Email Services: A Guide to True Email Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-01-06
How to Create a Personal Email Domain for Ultimate Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-02