9 Employee Onboarding Best Practices for 2025

A successful onboarding process is more than a first-day checklist; it's the critical foundation for employee engagement, productivity, and long-term retention. In modern work environments, effective onboarding must be strategic, structured, and secure, extending well beyond the initial week. A vital, yet often overlooked, component is establishing secure communication habits from day one. This involves not just setting up an email account but educating new hires on email privacy, security protocols, and the importance of using a secure hosted email platform to protect sensitive company data.
This article moves beyond generic advice to provide a comprehensive guide to employee onboarding best practices. We will explore 9 proven strategies that integrate deep cultural immersion with modern security needs, ensuring your new team members are not only productive but also confident and secure from their first interaction. Implementing these steps correctly is a direct investment in your workforce's success and longevity. Ultimately, the success of your onboarding program can be measured by its impact on employee longevity. Understanding how to reduce churn rate and boost retention starts with creating a powerful, supportive, and secure entry experience for every new hire.
1. Pre-boarding: Securely Engage Before Day One with Private Email Platforms
The period between a candidate's offer acceptance and their first day is a critical, yet often overlooked, part of the employee experience. This pre-boarding phase sets the tone for their entire tenure. One of the most impactful employee onboarding best practices is establishing a secure communication channel from the very beginning. Instead of exchanging sensitive documents like contracts, tax forms, and direct deposit information over insecure personal email accounts, leading companies are turning to private, hosted email platforms.

This approach immediately demonstrates a commitment to employee privacy and data security. By providing a temporary, secure email address through a service like Typewire, you create an encrypted environment for all pre-boarding activities. This not only protects the new hire's personally identifiable information (PII) but also introduces them to your company's security-first culture before they even step through the door. This initial focus on email security sets a critical precedent for all future communications.
How to Implement Secure Pre-boarding
Successfully integrating secure communication into your pre-boarding involves a few strategic steps:
- Provide a Secure Platform: Immediately after offer acceptance, create a temporary company email for the new hire on a private, hosted email platform. This ensures all subsequent communication is encrypted and secure.
- Communicate the "Why": Clearly explain that this measure is to protect their personal data. This builds trust and highlights your company's commitment to cybersecurity and email privacy.
- Deliver Technology Securely: If sending a company laptop, ensure it is fully configured with security software pre-installed. Send login credentials for the secure hosted email and other systems through a separate, secure channel.
- Assign a Secure Point of Contact: Designate an HR representative or onboarding buddy trained in email security protocols to handle any questions, ensuring consistent and safe communication.
2. Structured 90-Day Onboarding Plan
Effective onboarding extends far beyond the initial orientation week. A structured 90-day plan is one of the most crucial employee onboarding best practices, acting as a comprehensive roadmap for a new hire's first three months. This approach systematically builds their knowledge, skills, and integration into the company culture through distinct phases, ensuring they feel supported and can contribute meaningfully. Instead of overwhelming them with information upfront, a 90-day plan paces the learning curve and sets clear expectations.
This phased strategy, popularized by thought leaders like Michael D. Watkins in "The First 90 Days," provides a clear framework for success. By breaking the initial period into 30, 60, and 90-day segments, organizations can set specific, measurable goals for each stage. Companies like Salesforce and Meta use detailed programs that align learning modules and practical experience to these phases, transforming new hires into confident, productive team members.
This infographic outlines the sequential flow of a typical 90-day onboarding journey, highlighting the distinct focus of each 30-day phase.
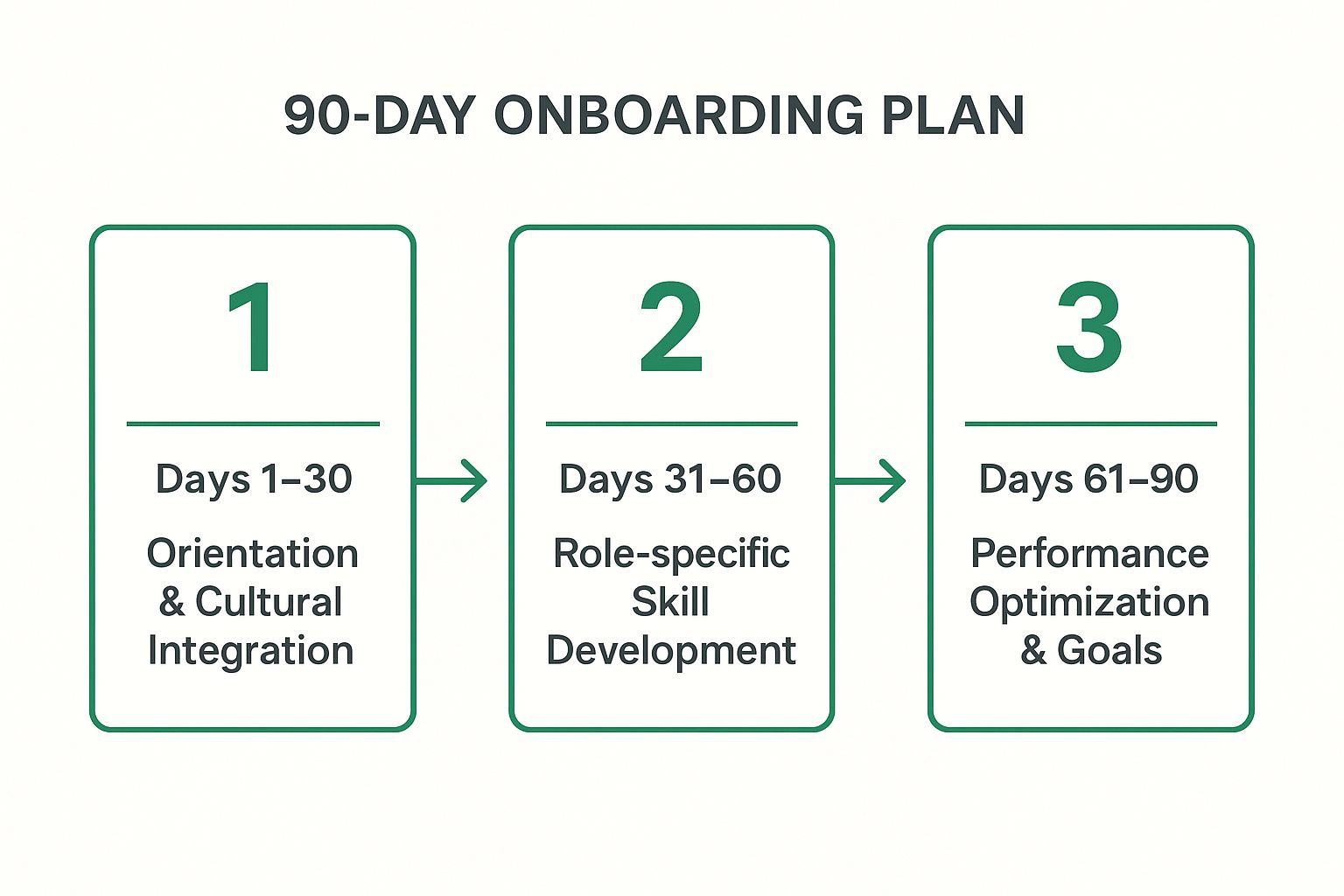
The visualization illustrates how the focus progressively shifts from foundational knowledge and cultural immersion to deep skill acquisition and, finally, to autonomous contribution and goal achievement.
How to Implement a 90-Day Onboarding Plan
Creating a successful 90-day plan requires thoughtful structure and consistent follow-through. Here are the key steps to implement this strategy effectively:
- Phase-Based Goals: Divide the plan into three 30-day stages. Focus the first month on cultural integration, foundational knowledge, and critical topics like email security best practices. The second month should center on role-specific training, and the third on performance optimization.
- Customize by Role: While core company-wide elements should remain consistent, tailor the plan’s technical training and performance milestones to the specific role and department.
- Schedule Regular Check-ins: Establish a cadence for formal check-ins at days 7, 30, 60, and 90. These meetings between the new hire and their manager are vital for assessing progress, providing feedback, and addressing any challenges.
- Incorporate Feedback Mechanisms: Build opportunities for new hires to provide feedback on the onboarding process itself. This continuous improvement loop helps refine the program for future employees.
3. Buddy/Mentor System
The transition into a new company can be overwhelming, filled with unspoken rules and operational nuances not found in any handbook. One of the most effective employee onboarding best practices is to implement a buddy or mentor system. This pairs a new hire with an experienced, non-supervisory colleague who acts as a go-to resource, cultural guide, and friendly face during the crucial first few months. This peer relationship provides a safe, informal channel for asking "silly" questions, understanding team dynamics, and accelerating social integration.

Unlike a manager, a buddy's primary role is support, not evaluation. This dynamic, popularized by companies like Google and Cisco, is proven to boost new hire satisfaction, productivity, and retention. For instance, Airbnb assigns buddies who take new hires to lunch on day one and meet weekly for the first month, creating an immediate sense of belonging. The system humanizes the onboarding process, transforming it from a checklist of tasks into a supported, relational experience.
How to Implement a Buddy/Mentor System
A successful buddy program is intentionally designed, not just improvised. It requires structure and clear communication to be effective.
- Select and Train Buddies: Choose buddies who are positive, knowledgeable, and possess strong communication skills. Provide them with a handbook outlining their role, expectations, and how to model good security practices, such as never sharing credentials via insecure channels.
- Make Thoughtful Pairings: Match new hires with buddies based on relevant factors like department, work style, or even shared interests to foster a stronger connection.
- Establish a Communication Cadence: Structure regular check-ins for the first few weeks, such as a daily coffee or a weekly lunch. After the initial period, these can transition to a more informal, as-needed basis.
- Encourage Informal Connections: The buddy's role is also to facilitate social integration. Encourage them to introduce the new hire to other team members and invite them to informal social gatherings.
- Gather Feedback: After the first 90 days, collect feedback from both the new hire and the buddy to continuously refine and improve the program for future employees.
4. Role-Specific Training and Skill Development
While a general company orientation is crucial, one of the most vital employee onboarding best practices is to move quickly into targeted, role-specific training. This phase goes beyond cultural immersion to equip new hires with the precise technical skills, process knowledge, and job-specific competencies they need to excel. It bridges the gap between understanding the company's mission and being able to actively contribute to it through their unique function.
This tailored approach ensures employees aren't left to figure things out on their own, which can lead to errors, decreased confidence, and slower ramp-up times. By providing a structured learning path that includes critical topics like data handling and email security protocols, you empower them to become proficient and productive much faster. For example, Salesforce’s "Trailhead" offers customized learning modules for every function, ensuring each new hire receives relevant and immediately applicable training.
How to Implement Role-Specific Training
Building an effective role-specific training plan requires a structured approach focused on practical application:
- Analyze the Role: Conduct a job task analysis to identify the critical skills, tools, and knowledge areas essential for success. This must include training on secure use of communication tools, especially their hosted email platform.
- Sequence the Learning: Structure training logically, starting with foundational concepts and gradually moving to more advanced, complex tasks. This prevents overwhelming the new employee.
- Prioritize Hands-On Practice: Move beyond theory by incorporating simulations, real-world task assignments, and interactive exercises. Learning by doing solidifies understanding of both job tasks and security protocols.
- Leverage Shadowing: Arrange for the new hire to shadow experienced team members. This provides valuable context and demonstrates how processes, including secure data handling, work in real-time.
- Establish Feedback Loops: Build in regular check-ins and skill assessments to gauge progress, answer questions, and provide constructive feedback, ensuring the employee stays on the right track.
5. Cultural Immersion and Values Integration
A new hire’s long-term success often depends less on their technical skills and more on their ability to align with the company's culture. One of the most critical employee onboarding best practices is to move beyond procedural training and intentionally immerse new hires in your organization's values, mission, and behavioral norms. This practice ensures employees understand not just what to do, but how and why things are done within your unique environment.
True cultural integration goes far beyond a single presentation. It involves weaving your company's core principles into every aspect of the onboarding experience. If email privacy and data security are core values, this should be a central theme. For example, Netflix famously dedicates significant time to discussing its culture deck, focusing on concepts like freedom and responsibility. This approach helps new employees become not just productive team members, but genuine cultural contributors who understand the values driving key business decisions.
How to Implement Cultural Immersion
Successfully integrating new hires into your company culture requires a deliberate and multi-faceted strategy:
- Lead with Storytelling: Instead of just listing company values, have leaders share stories that demonstrate them in action. Include examples of how a commitment to email security protected the company or a client.
- Create Experiential Opportunities: Design activities that allow new hires to experience the culture firsthand. This could be a problem-solving session that requires secure collaboration or a group volunteer day aligned with your mission.
- Connect Roles to the Bigger Picture: Clearly articulate how each new hire’s specific role contributes to the organization's overarching mission, including their responsibility in maintaining data privacy and security.
- Make Culture a Continuous Conversation: Don't limit culture discussions to a single onboarding session. Use team meetings to reinforce values, discuss how they apply to daily work, and encourage open dialogue about topics like email privacy.
6. Manager Enablement and Accountability
While HR often coordinates the onboarding process, the direct manager is the single most influential person in a new hire's success. Manager enablement and accountability is an employee onboarding best practice that shifts primary responsibility from HR to the team leader. This approach recognizes that managers are best positioned to integrate new hires into their specific team culture, roles, and workflows, but they need dedicated support to do so effectively. It involves equipping them with the tools, training, and clear expectations necessary to deliver a consistent, high-impact onboarding experience.
This strategy moves beyond simply sending managers a reminder email. It involves a systemic approach where managers are trained, resourced, and held accountable for the integration and initial performance of their team members. Companies like Google and Microsoft have invested heavily in this area, recognizing that an empowered manager directly translates to higher new hire retention, faster ramp-up times, and greater long-term engagement. The goal is to make great onboarding, including reinforcement of email security policies, a core managerial skill.
How to Implement Manager Enablement
Building a manager-led onboarding program requires a clear framework and dedicated resources to ensure consistency and quality:
- Develop a Manager's Playbook: Create a simple, actionable playbook that outlines key activities. Include prompts for discussing the importance of the company's hosted email platform and secure communication habits.
- Provide Proactive Training: Train managers on effective onboarding before their new hire starts. This should cover coaching, providing feedback, and reinforcing security policies.
- Establish Accountability Metrics: Integrate onboarding effectiveness into manager performance reviews. Use new hire feedback surveys to specifically ask about their manager's support, including guidance on security and communication tools.
- Automate Key Reminders: Use your HRIS or communication tools to send automated reminders to managers for critical milestones, such as scheduling the 30-day check-in or reviewing security protocols.
7. Technology and Digital Onboarding Tools
In today's digital-first environment, relying on manual processes and paperwork for onboarding is inefficient and creates a disjointed experience. A key employee onboarding best practice is leveraging technology and digital tools to streamline, automate, and personalize the new hire journey. This approach utilizes integrated software solutions like onboarding portals, which can be linked to secure, private hosted email platforms to ensure data integrity from the start.
Digital onboarding tools automate administrative tasks, deliver consistent training (including email security modules), and track progress, which is particularly vital for remote and hybrid teams. Companies like Hilton have used this strategy to reduce time-to-productivity by 30% with interactive training modules. This tech-enabled approach frees up HR and managers to focus on high-impact, human-centric activities, ensuring new hires feel supported and productive from their first interaction.
How to Implement Digital Onboarding Tools
Integrating technology effectively requires a strategic approach that balances automation with human connection:
- Integrate Your Tech Stack: Choose platforms that connect seamlessly. For instance, your onboarding tool should integrate with your IT provisioning system to automatically create a secure account on your hosted email platform.
- Prioritize User Experience: Select tools that are intuitive and mobile-accessible. A secure but difficult-to-use platform can hinder adoption. For organizations seeking to implement cutting-edge solutions, exploring the 12 Best Employee Onboarding Software Options can provide a strong starting point.
- Start Small and Scale: Begin by automating core processes like paperwork completion and compliance training, including mandatory email security courses.
- Use Analytics to Improve: Leverage data from your onboarding platform to see where new hires get stuck. Use these insights to refine the digital experience, especially around security and tool adoption.
8. Regular Check-ins and Feedback Loops
Effective onboarding is not a single event but a continuous process. One of the most critical employee onboarding best practices is to move beyond a "set it and forget it" mentality by establishing structured, regular check-ins. These planned conversations create an ongoing feedback loop where new hires, managers, and HR can discuss progress, resolve challenges, and fine-tune the onboarding experience in real-time. This ensures new team members feel consistently supported and heard.
This approach transforms onboarding from a passive information dump into an active, responsive dialogue. By scheduling touchpoints at key milestones, companies can proactively address issues, including any confusion about communication tools or security policies, before they escalate. This strategy is exemplified by companies like Adobe, which integrated its continuous "Check-In" conversation model directly into its onboarding, fostering a culture of feedback from the very beginning.
How to Implement Regular Check-ins
Building a successful feedback loop requires structure and commitment. It’s about creating a safe, consistent space for open communication.
- Schedule in Advance: Treat check-ins as non-negotiable appointments. Add them to calendars for the new hire and their manager during the first week to signal their importance.
- Use Conversation Guides: Provide managers with a simple framework. Include questions like, "Do you have any questions about our email privacy policy?" or "Are you comfortable using our secure communication tools?"
- Foster Psychological Safety: Initially, separate these check-ins from formal performance evaluations. Frame them as supportive conversations aimed at helping the new hire succeed and improving the process for future employees.
- Document and Follow Up: Record key takeaways and action items. Following through on commitments, such as providing additional training on the hosted email platform, demonstrates that the feedback is valued.
9. Socialization and Network Building
An employee's success is defined not just by their skills, but by their ability to navigate the organization's social fabric and build a strong professional network. A key component of employee onboarding best practices is to intentionally facilitate socialization and relationship-building. This process helps new hires understand who to approach for information, support, and collaboration, accelerating their integration and sense of belonging. Without structured guidance, new employees can feel isolated, which hinders both productivity and long-term retention.

This practice moves beyond simple team introductions to create a strategic web of connections. Companies like LinkedIn encourage new hires to set up 10-15 coffee chats across different departments in their first month. Similarly, Shopify's remote onboarding includes virtual social hours and randomized coffee pairings to foster community among a distributed workforce. These activities are designed to build social capital, making new team members feel seen, supported, and connected to the company's mission and culture from the very beginning.
How to Implement Socialization and Network Building
Integrating structured networking into your onboarding program requires a deliberate and inclusive approach:
- Curate a Connection List: Provide new hires with a suggested list of key people to meet. Include names, roles, and a brief note on why connecting with them is valuable, especially key contacts in IT for security questions.
- Facilitate Warm Introductions: Have the manager or onboarding buddy make the initial introductions, either in person or via the company's secure hosted email platform. This removes awkwardness and reinforces proper communication channels.
- Schedule Social Time: Formally block out time in the onboarding schedule for non-work activities like team lunches or virtual coffee chats. This signals that building relationships is a valued part of the job.
- Leverage Technology: Use collaboration tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams to create dedicated channels for new hire cohorts. For remote teams, utilize virtual chat tools to randomly pair employees for informal conversations.
Employee Onboarding Best Practices Comparison
| Onboarding Approach | Implementation Complexity  |
Resource Requirements  |
Expected Outcomes  |
Ideal Use Cases  |
Key Advantages  |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-boarding: Engage Before Day One | Moderate – requires upfront coordination | Moderate – communications, IT, and logistics | Higher engagement, reduced turnover, faster ramp-up | New hires before start date; remote employee setups | Reduces first-day admin; builds excitement early |
| Structured 90-Day Onboarding Plan | High – needs detailed planning & updates | High – manager time, documentation, training | Clear milestones, better retention, time-to-productivity reduced | All roles needing phased onboarding | Provides clarity, accountability, and measurable progress |
| Buddy/Mentor System | Moderate – depends on buddy training | Moderate – buddy time and training | Faster cultural integration, higher satisfaction | Social support-focused roles, team integration | Safe space for questions, reduces manager burden |
| Role-Specific Training and Skill Development | High – content development & updates | High – training materials, trainers, assessments | Faster competency, fewer errors, consistent quality | Technical or specialized roles | Accelerates skill acquisition, builds confidence |
| Cultural Immersion and Values Integration | Moderate – needs authentic leadership involvement | Moderate – training, storytelling, activities | Stronger cultural fit, increased engagement | Organizations emphasizing cultural alignment | Builds belonging and decision-aligned behaviors |
| Manager Enablement and Accountability | High – ongoing manager training & monitoring | Moderate to High – manager time & HR support | Higher retention, better engagement, consistent onboarding | Manager-led onboarding environments | Leverages managers’ role, improves leadership |
| Technology and Digital Onboarding Tools | High – software investment and integration | High – platforms, maintenance, training | Reduced admin time, scalable onboarding, consistent experience | Large-scale, remote/hybrid workforce | Automates admin, improves self-service & analytics |
| Regular Check-ins and Feedback Loops | Moderate – scheduling and training required | Moderate – manager and HR time | Early issue resolution, higher engagement, continuous improvement | All onboarding phases needing iterative support | Creates dialogue, strengthens relationships |
| Socialization and Network Building | Moderate – needs facilitation & events | Moderate – event planning, coordination | Increased belonging, collaboration, and retention | Roles needing strong informal networks | Builds social capital, reduces isolation |
Onboarding as Your First Line of Defense
Transitioning from a promising candidate to a high-performing team member is a journey, not a single event. The difference between an employee who thrives and one who struggles often comes down to the quality of their initial experience. By moving beyond a simple checklist-driven orientation, you can build a comprehensive onboarding program that serves as a strategic asset for your entire organization. Implementing these employee onboarding best practices is your first, and most critical, line of defense in building a resilient, engaged, and security-conscious workforce.
Weaving Security and Culture into Your Foundation
The nine practices detailed in this guide, from a robust pre-boarding process to a structured 90-day plan, are designed to work in concert. A buddy system fosters connection, while manager enablement ensures consistent support. Technology and digital tools streamline logistics, allowing more time for the crucial human elements: cultural immersion, regular feedback, and network building.
Crucially, modern onboarding must address the digital realities of today's workplace. This is where the principles of email privacy and security become paramount. By introducing new hires to your company's secure communication protocols from day one, you are not just teaching them a process; you are embedding a core value. Using a secure hosted email platform sets the standard, demonstrating that protecting company and client data is non-negotiable.
From Process to Strategic Advantage
Ultimately, a world-class onboarding program delivers tangible business results. It accelerates the time to productivity, significantly improves employee retention rates, and strengthens your company culture with every new hire. When an employee feels supported, understands their role, and is equipped with the right tools and security knowledge, they are empowered to do their best work. This isn't just about making a good first impression; it's about setting a long-term trajectory for success, both for the individual and the company.
Your next steps should involve a candid assessment of your current process against these best practices.
- Identify Gaps: Where does your current onboarding fall short? Are you leveraging a secure, hosted email platform from day one? Do managers have the resources they need to reinforce email security?
- Prioritize a Pilot: You don't need to overhaul everything at once. Choose one or two high-impact areas, like implementing a secure pre-boarding process or creating role-specific security training modules, and start there.
- Integrate Security: Review how you introduce new hires to your communication and security policies. Ensure they understand not just the "how" but the "why" behind using secure tools and practices like a private hosted email.
By viewing onboarding as a continuous, strategic function, you transform it from a procedural necessity into a powerful engine for growth, security, and cultural cohesion. The investment you make in those first 90 days will pay dividends for years to come, building a team that is not only effective but also a first line of defense in protecting your organization's most valuable assets.
Ready to build your security-first onboarding process from the ground up? A secure hosted email platform is the perfect starting point. Typewire provides the ad-free, no-tracking email infrastructure you need to protect your team’s communications and set a high standard for data privacy from day one. Learn more about Typewire and secure your communications today.
9 Employee Onboarding Best Practices for 2025
Posted: 2025-10-07
The 12 Best Email Clients for Mac in 2026: A Guide to Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-02-24
Professional Email Addresses: Your First Line of Defense for Trust and Security
Posted: 2026-02-21
How Do I Block Gmail and Reclaim Your Inbox Privacy
Posted: 2026-02-17
7 Top Canadian Tech Companies Leading in Privacy and Security for 2026
Posted: 2026-02-13
Professional Email Greeting: Master the professional email greeting today
Posted: 2026-02-10
What is Email Phishing: Securing Your Inbox Against Digital Fraud
Posted: 2026-02-06
10 Email Retention Policy Best Practices for Security and Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-02-03
Top 12 Secure Alternatives to Gmail for Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-01-31