GDPR Compliance Checklist: Ensure Your Data Privacy Success

Navigating GDPR in 2025: A Simple Checklist
This GDPR compliance checklist simplifies the essential steps for safeguarding personal data and ensuring your business operates within the law. From data mapping to security measures, these seven points provide actionable insights to help you meet GDPR requirements. Non-compliance can lead to significant fines and reputational damage, so understanding these core concepts is crucial for every business handling personal data. This list covers data processing inventory, privacy notices and consent, data subject rights procedures, data protection impact assessments (DPIAs), data breach response plans, vendor management, and technical and organizational security measures.
1. Data Processing Inventory and Mapping
Creating a Data Processing Inventory and Mapping is the crucial first step in any GDPR compliance checklist. This foundational element involves documenting all processing activities related to personal data within your organization. It provides a comprehensive overview of what data you collect, why you collect it, how it's processed, where it's stored, and who has access to it. This deep understanding of your data landscape is not just a good practice, but a requirement under Article 30 of the GDPR. Without this inventory, demonstrating compliance and effectively responding to data subject requests becomes incredibly difficult.
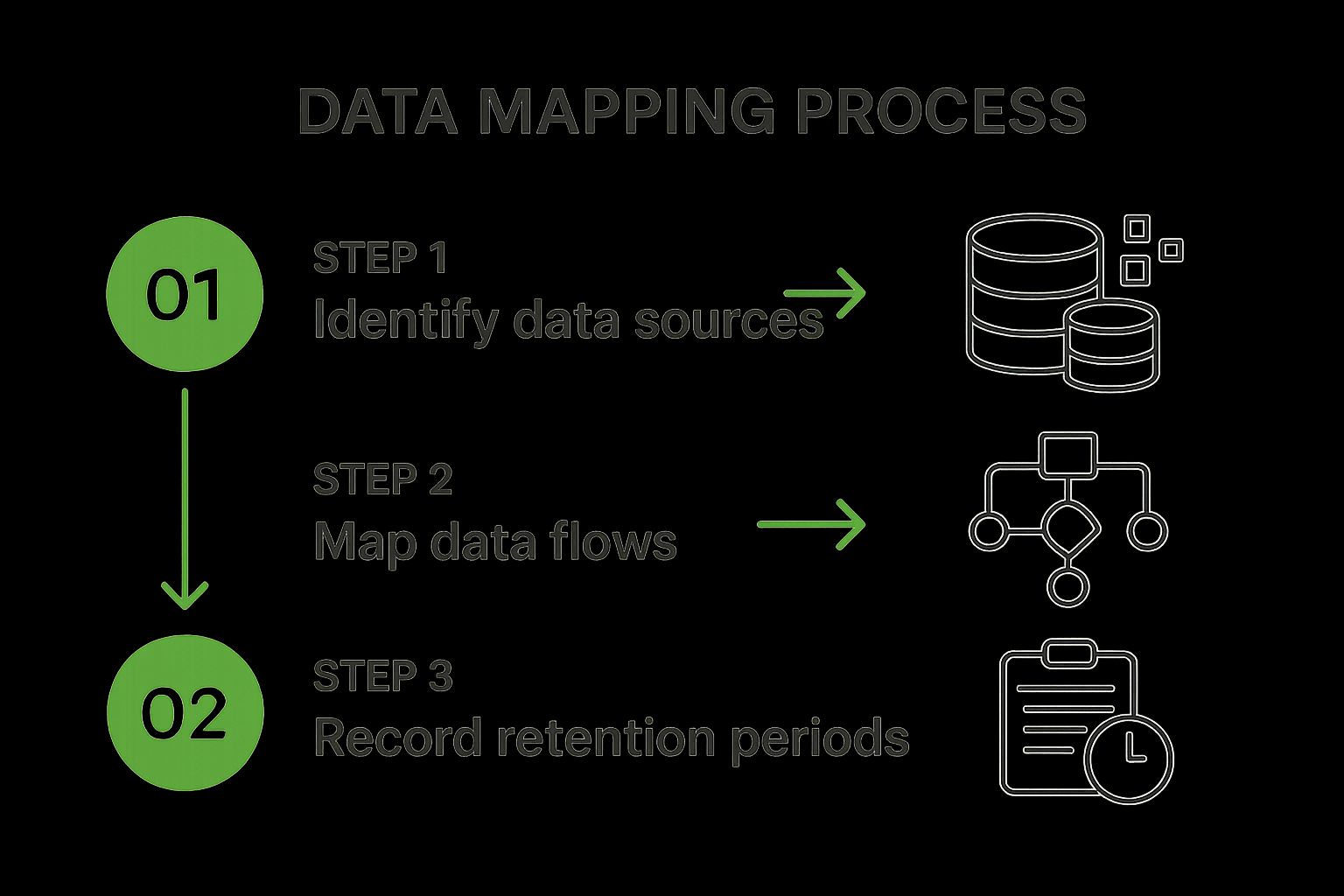
The infographic above visualizes the key stages involved in Data Processing Inventory and Mapping. It starts with identifying the purpose of processing, followed by determining the categories of data involved and the legal basis for processing. It then highlights the importance of mapping data flows and defining storage locations and retention periods. Finally, it emphasizes the ongoing need for review and updates. This cyclical process ensures that your data inventory remains accurate and relevant.
This methodical approach provides several key features, including comprehensive documentation of data flows, identification of data controllers and processors, classification of personal data types (e.g., standard vs. special categories), documentation of the legal basis for processing (e.g., consent, contract, legal obligation), and a record of data retention periods.
The following steps outline the process illustrated in the infographic, which is essential for creating and maintaining a GDPR-compliant Data Processing Inventory and Mapping:
- Identify Purpose of Processing: Define why you are collecting and processing personal data. Be specific about each purpose.
- Determine Data Categories: Categorize the types of personal data you process. Identify any special category data (e.g., health, biometric, or religious data).
- Establish Legal Basis: Determine the legal basis for processing each category of data (e.g., consent, contractual necessity, legal obligation).
- Map Data Flows: Document how data moves within your organization, including internal transfers and external transfers to third parties.
- Define Storage and Retention: Specify where data is stored and for how long. Ensure your retention policies align with legal obligations and business needs.
- Review and Update: Regularly review and update your data inventory to reflect changes in your processing activities.
The sequence of these steps is crucial because each step builds upon the previous one. For example, without a clear understanding of the purpose of processing (step 1), it’s impossible to determine the appropriate legal basis (step 3) or define suitable retention periods (step 5). This structured approach ensures a comprehensive and legally sound data inventory.
Companies like Airbnb and Siemens have successfully implemented data inventory and mapping. Airbnb created detailed data maps illustrating the flow of customer information through their booking platform. Siemens developed a comprehensive data inventory across all business units using specialized GDPR compliance software.
Pros:
- Provides visibility into data processing activities.
- Helps identify compliance gaps and risks.
- Facilitates responses to Data Subject Requests (DSRs).
- Serves as evidence of compliance to supervisory authorities.
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming, especially for large organizations.
- Requires regular updates as data processing activities change.
- May reveal uncomfortable compliance gaps.
Tips for Implementation:
- Start with interviews across departments to understand data flows.
- Use data discovery tools to automatically identify personal data repositories.
- Create visual data flow diagrams for easier understanding.
- Prioritize high-risk processing activities.
- Review and update the inventory at least annually.
This approach is essential for any organization processing personal data of EU residents. It forms the bedrock of GDPR compliance and allows you to demonstrate accountability. This is why Data Processing Inventory and Mapping deserves its place at the top of any GDPR compliance checklist. The Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) in the UK and the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) have both highlighted the importance of this crucial step.
This video provides further insights into data mapping and its role in GDPR compliance.
2. Privacy Notices and Consent Management
A crucial aspect of any GDPR compliance checklist is Privacy Notices and Consent Management. This involves developing and implementing clear, transparent privacy notices and robust consent management mechanisms. This ensures individuals are properly informed about how their data is used and provides valid mechanisms for obtaining and managing consent where necessary for data processing activities. This component of GDPR compliance not only fulfills legal obligations but also builds trust with users and minimizes the risk of complaints and regulatory actions. It sits at the heart of a transparent and ethical approach to data handling.

Key features of effective privacy notices and consent management within a gdpr compliance checklist include layered privacy notices written in plain language, just-in-time notifications for data collection, dedicated consent management systems, meticulous record-keeping of consent, and readily accessible mechanisms for users to withdraw their consent. Creating a comprehensive privacy notice is crucial, but it's just one part of a larger strategy. To truly protect user data and maintain GDPR compliance, you need a holistic approach. For a deeper dive into building a comprehensive strategy, resources like a robust data privacy compliance framework from Whisperit can provide valuable guidance.
Successful implementations of this approach are evident in organizations like the BBC, which redesigned their privacy notices using a layered approach and clear language, making it easier for users to understand how their data is being used. Mastercard provides another excellent example, having implemented a consent management platform that tracks consent across all customer touchpoints. These examples showcase how large organizations prioritize transparent data practices.
Why Use This Approach?
This item deserves its place in the gdpr compliance checklist because it directly addresses core principles of the GDPR: transparency and user control. By clearly communicating data processing activities and providing mechanisms for consent management, organizations empower users to make informed decisions about their data.
Pros:
- Builds trust with data subjects
- Reduces risk of complaints and regulatory actions
- Creates transparency in data processing
- Enables demonstrable compliance
Cons:
- Can create friction in user experience
- Requires regular updates as processing activities change
- Technical implementation challenges for consent tracking
Actionable Tips:
- Layered Privacy Notices: Use a summary layer for quick overviews and a detailed layer for comprehensive information.
- User Testing: Test your privacy notices with actual users to ensure they are easily understood.
- Consent Dashboards: Implement consent dashboards to give users control over their data preferences.
- Consent Management Platforms (CMPs): Utilize CMPs for websites to streamline the consent process.
- Documentation: Thoroughly document the design decisions behind your consent mechanisms for auditing and compliance purposes.
This approach is relevant for any organization that collects and processes personal data from individuals within the European Union, regardless of size or industry. It is a fundamental requirement for GDPR compliance and a best practice for building trust and transparency with users. Organizations like the Information Commissioner's Office (ICO), as well as leading consent management platforms like OneTrust and TrustArc, have popularized and championed these practices.
3. Data Subject Rights Procedures
A crucial element of any GDPR compliance checklist is establishing robust Data Subject Rights (DSR) procedures. This involves creating clear processes and systems for handling requests from individuals (data subjects) who want to exercise their rights concerning their personal data. These rights include:
- Access: The right to obtain confirmation that their data is being processed and to access that data.
- Rectification: The right to have inaccurate personal data corrected.
- Erasure ("Right to be forgotten"): The right to have their personal data deleted under certain circumstances.
- Restriction of Processing: The right to limit how their data is processed.
- Portability: The right to receive their personal data in a structured, commonly used, and machine-readable format and to transmit that data to another controller.
- Objection: The right to object to the processing of their personal data under certain circumstances.
Effectively managing DSR requests is not only legally mandated for GDPR compliance but also fosters trust with your customers and demonstrates a commitment to data privacy. Without clear procedures, organizations risk non-compliance, potential fines, and reputational damage.
How Data Subject Rights Procedures Work:
DSR procedures typically involve a multi-step process:
- Request Intake and Verification: Receiving requests through designated channels (e.g., online forms, dedicated email address) and verifying the identity of the requester.
- Request Assessment: Determining the validity and scope of the request based on the specific right invoked and the legal basis for processing.
- Response and Fulfillment: Taking appropriate action based on the request, such as providing data access, rectifying information, or deleting data.
- Documentation and Tracking: Maintaining records of all requests received, actions taken, and justifications for any denials.
Features of Effective DSR Procedures:
- Request Intake and Verification System: A centralized system for receiving and authenticating requests.
- Response Templates for Different Rights: Pre-written templates to ensure consistent and accurate communication.
- Tracking System for Request Deadlines: Tools to monitor deadlines and ensure timely responses (generally one month under GDPR).
- Cross-functional Workflows for Fulfillment: Processes that involve relevant teams (e.g., IT, legal, customer service) to efficiently fulfill requests.
- Documentation of All Actions Taken: A comprehensive audit trail for accountability and demonstrating compliance.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Microsoft: Provides a dedicated privacy dashboard allowing users to access, manage, and delete their data across various Microsoft services.
- Spotify: Offers automated data portability tools that enable users to download their data in machine-readable formats.
Pros:
- Ensures consistent and compliant handling of DSR requests.
- Reduces response time and resources needed.
- Demonstrates accountability to regulators.
- Improves customer trust and satisfaction.
Cons:
- Can be resource-intensive for complex requests.
- May require significant system changes.
- Potential business impact of deletion requests (e.g., loss of valuable customer data).
Tips for Implementing DSR Procedures:
- Centralize the intake of requests through a dedicated form or email address.
- Create decision trees for different types of requests to guide appropriate action.
- Develop templates for responding to common requests to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Train customer service teams on handling rights requests.
- Set up reminders to meet the one-month response deadline.
- Document justifications for any request denials.
Popularized By:
The importance of DSR procedures has been emphasized by the European Data Protection Board (EDPB) and legal challenges brought by privacy activists like Max Schrems, whose work has significantly shaped DSR implementation.
Including Data Subject Rights Procedures in your GDPR compliance checklist is essential for fulfilling legal obligations, building trust with customers, and demonstrating a commitment to data privacy. By implementing clear processes and utilizing available tools, organizations can effectively manage DSR requests and minimize the risks associated with non-compliance.
4. Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs)
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) are a crucial element of any GDPR compliance checklist. They represent a structured process for identifying and minimizing data protection risks associated with high-risk processing activities. Essentially, DPIAs help organizations proactively assess the potential privacy implications before implementing new systems, processes, or technologies involving personal data. This preemptive approach is particularly important when dealing with new technologies, large-scale data processing, or sensitive personal data like health information, biometric data, or political opinions. Including DPIAs in your GDPR compliance strategy demonstrates a commitment to data protection and helps avoid potential legal issues and reputational damage.
How DPIAs Work:
A DPIA is a systematic process involving several key steps:
- Systematic description of processing operations: Clearly define the purpose, scope, and data flows involved in the processing activity.
- Assessment of necessity and proportionality: Justify the need for the processing and ensure it's proportionate to the intended purpose. Avoid collecting more data than necessary.
- Risk identification and evaluation: Identify potential risks to individuals' rights and freedoms arising from the processing, considering the likelihood and severity of potential harm.
- Risk mitigation measures: Develop and implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to mitigate identified risks. This might include data anonymization, encryption, or access controls.
- Documentation of decision-making: Maintain comprehensive records of the DPIA process, including the identified risks, mitigation measures, and justifications for decisions.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several organizations have effectively implemented DPIAs to ensure GDPR compliance:
- The UK National Health Service (NHS) conducts DPIAs for all new healthcare data initiatives, ensuring patient privacy is protected in sensitive medical research and data analysis projects.
- Facebook performed extensive DPIAs before launching facial recognition features in Europe, a technology with significant privacy implications.
When and Why to Use DPIAs:
GDPR Article 35 outlines specific situations requiring a DPIA. These typically involve:
- Systematic and extensive evaluation of personal aspects relating to natural persons: This includes profiling and predicting behavior.
- Processing on a large scale of special categories of data: This includes sensitive data like health, biometric, or genetic data.
- Systematic monitoring of publicly accessible areas on a large scale: For instance, using CCTV for widespread surveillance.
Even if your processing activities don't strictly fall under these categories, conducting a DPIA can be a valuable exercise for any project involving personal data.
Pros and Cons of DPIAs:
Pros:
- Identifies risks early in project development, preventing costly redesigns later.
- Demonstrates compliance through documented evidence.
- Helps build privacy by design principles into systems and processes.
- Can prevent costly redesigns and legal issues later.
Cons:
- Can delay project implementation if not planned effectively.
- Requires specialized privacy expertise.
- May reveal significant compliance challenges requiring project changes.
Actionable Tips for Conducting DPIAs:
- Integrate DPIA screening questions into project management workflows: This helps identify projects requiring DPIAs early on.
- Develop templates tailored to different types of processing: Streamline the DPIA process and ensure consistency.
- Involve diverse stakeholders including IT, legal, and business units: Gain a comprehensive understanding of the processing activity and potential risks.
- Consider using specialized DPIA software tools: Automate certain tasks and improve efficiency.
- Review DPIAs periodically as processing activities evolve: Ensure ongoing compliance as technologies and processes change.
- Document consultation with the Data Protection Officer (DPO) on high-risk findings: Demonstrate collaboration and accountability.
By incorporating DPIAs into your GDPR compliance strategy, you proactively address potential privacy risks, demonstrate a commitment to data protection, and contribute to a culture of privacy within your organization.
5. Data Breach Response Plan
A crucial component of any GDPR compliance checklist is a robust Data Breach Response Plan. This documented protocol outlines the procedures for detecting, reporting, containing, and remediating personal data breaches. It ensures organizations can respond quickly and effectively to such incidents, minimizing the harm to data subjects and meeting the GDPR's stringent 72-hour notification requirement. Without a plan, organizations risk significant regulatory penalties and reputational damage. This is why a Data Breach Response Plan deserves a prominent place on your GDPR compliance checklist.

A comprehensive Data Breach Response Plan incorporates several key features: robust breach detection mechanisms to identify incidents promptly; a severity assessment framework to categorize breaches based on their potential impact; clear internal notification procedures to escalate incidents efficiently; pre-prepared documentation templates for reporting to authorities and individuals; external communication plans to manage public relations and stakeholder engagement; and a post-breach review process to identify vulnerabilities and improve future responses. These features work together to create a streamlined and effective response process.
The benefits of implementing a Data Breach Response Plan are substantial. It reduces the time taken to respond to breaches, minimizing potential regulatory penalties, which can be significant under the GDPR. It provides clarity and direction during crisis situations, ensuring a coordinated and controlled response. Furthermore, a well-executed plan demonstrates accountability to regulators and builds trust with data subjects.
Examples of real-world breach responses highlight the importance of preparedness. Marriott's response to their 2018 Starwood breach, while following a comprehensive plan, still resulted in a substantial £18.4m fine, illustrating the severity of GDPR enforcement. Equifax, following their 2017 breach, implemented an enhanced breach response program, demonstrating the importance of continuous improvement in this area.
While beneficial, a Data Breach Response Plan does have some potential drawbacks. It requires regular testing and updating to remain effective, which can be resource-intensive. The process of developing a plan may reveal existing security weaknesses, requiring further investment in security measures. Furthermore, implementing a consistent plan across multiple jurisdictions can be challenging due to varying legal requirements.
Actionable Tips for Implementing a Data Breach Response Plan:
- Form a cross-functional incident response team: Define clear roles and responsibilities for each member, ensuring a coordinated response.
- Create breach severity assessment criteria: Establish clear criteria to categorize breaches based on the number of individuals affected, the sensitivity of the data involved, and the potential impact.
- Develop templates for regulatory notifications: Prepare templates for notifying supervisory authorities and affected individuals, ensuring compliance with GDPR notification requirements.
- Conduct regular tabletop exercises: Test the plan regularly through simulated breach scenarios to identify gaps and improve response effectiveness.
- Establish relationships with forensic experts in advance: Having pre-existing relationships with forensic specialists ensures quick access to expert assistance during a breach.
- Document all breach response actions: Maintain detailed records of all actions taken during the response process to provide evidence of compliance to regulatory authorities.
Organizations should use this approach as a proactive measure, before a breach occurs. By having a plan in place, organizations can minimize the negative consequences of a data breach and demonstrate their commitment to data protection under the GDPR. The Information Commissioner's Office (ICO) and ENISA (European Union Agency for Cybersecurity) are key resources and advocates for the development and implementation of robust Data Breach Response Plans. By prioritizing this element of GDPR compliance, organizations can protect themselves, their data subjects, and their reputation.
6. Vendor Management and Data Processing Agreements
A crucial aspect of GDPR compliance lies in managing your third-party vendors, especially those who process personal data on your behalf. This element of your GDPR compliance checklist, Vendor Management and Data Processing Agreements (DPAs), establishes a systematic approach to ensure these external organizations adhere to the regulation's stringent requirements. This isn't just a box to check; it's a fundamental practice for protecting the personal data you handle and maintaining the trust of your users. Without robust vendor management, your organization's overall GDPR compliance is significantly weakened.
How it Works:
Vendor management for GDPR compliance involves identifying all third-party vendors that process personal data, assessing the risks associated with their processing activities, and implementing legally binding DPAs. These agreements outline the responsibilities of both parties regarding data protection, including data security, confidentiality, and the rights of data subjects. Ongoing monitoring and management of these vendors, including their subprocessors, are essential for maintaining continued compliance. This process also needs to account for international data transfers, ensuring appropriate safeguards are in place.
Features of Effective Vendor Management:
- Vendor Risk Assessment Process: Categorizing vendors based on the type and sensitivity of data they process allows for a tiered approach to risk management.
- GDPR-Compliant Data Processing Agreements (DPAs): These legally binding contracts specify the roles and responsibilities of both parties concerning data protection.
- Ongoing Monitoring Mechanisms: Regular audits and reviews ensure vendors maintain compliance over time.
- Subprocessor Management: Understanding and managing the vendors your vendors use is crucial for complete oversight.
- International Data Transfer Safeguards: Implementing appropriate measures like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) when data leaves the EEA.
Pros:
- Extends GDPR compliance to your supply chain: Ensuring data protection throughout your entire operation.
- Clarifies responsibilities between parties: Leaving no room for ambiguity about who is responsible for what.
- Provides legal recourse in case of vendor non-compliance: Offering a framework for addressing breaches and violations.
- Creates transparency in data processing activities: Providing a clear picture of how and where data is being processed.
Cons:
- Time-consuming to implement with existing vendors: Requires significant effort to update existing agreements and processes.
- May require renegotiation of contracts: Existing contracts may not meet GDPR requirements and need amendments.
- Complex to manage for organizations with many vendors: Tracking and managing compliance across a large vendor base can be challenging.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Salesforce: Developed standardized GDPR-compliant DPAs, streamlining the process for all their customers.
- Philips: Implemented a comprehensive vendor risk management program with tiered assessment based on data sensitivity, demonstrating a proactive approach to compliance.
Actionable Tips:
- Create a vendor inventory categorizing processors by risk level. This helps prioritize your efforts and allocate resources effectively.
- Develop standard DPA templates for different vendor types. This simplifies the process and ensures consistency across agreements.
- Implement right to audit provisions in all agreements. This allows you to verify vendor compliance directly.
- Verify vendors' technical and organizational measures. Ensure they have adequate security controls in place.
- Maintain records of all international data transfers. Documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance.
- Schedule regular compliance reviews for critical vendors. Don't just set it and forget it; actively monitor ongoing compliance.
Why This Item Deserves Its Place in the GDPR Compliance Checklist:
Vendor management and DPAs are non-negotiable for GDPR compliance. Any organization that uses third-party processors to handle personal data must have these mechanisms in place. Failure to do so exposes the organization to significant legal and financial risks, including substantial fines and reputational damage. By including this item in your GDPR compliance checklist, you acknowledge the importance of extending data protection principles beyond your organization's walls and into your entire processing ecosystem. This is a proactive step towards building trust with your customers and demonstrating your commitment to data protection.
7. Technical and Organizational Security Measures
This crucial aspect of GDPR compliance, focusing on technical and organizational security measures, ensures the protection of personal data against unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. It's a core component of any robust GDPR compliance checklist because it addresses the practical "how" of safeguarding data. Simply put, it's about putting systems and processes in place to keep personal data safe and demonstrate your commitment to GDPR principles. This item deserves its place on the list because it directly addresses the GDPR's requirements for data security and demonstrates proactive efforts towards compliance.
This encompasses both technological safeguards and organizational strategies. Think of it as a two-pronged approach: the technical side involves implementing security controls like encryption and access management, while the organizational side focuses on processes like security training and incident response planning. Both are essential for achieving comprehensive data protection and demonstrating compliance with the GDPR.
Features of Robust Technical and Organizational Security Measures:
- Data encryption (in transit and at rest): Encrypting data both while it's being transmitted and while it's stored ensures that even if a breach occurs, the data itself remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Access controls and authentication: Limiting access to personal data based on the principle of least privilege and implementing strong authentication methods (like multi-factor authentication) minimizes the risk of unauthorized access.
- Security monitoring and logging: Continuously monitoring systems for suspicious activity and maintaining detailed logs enables early detection of potential breaches and provides valuable evidence for investigations.
- Vulnerability management: Regularly scanning for and patching system vulnerabilities proactively reduces the attack surface and minimizes the risk of exploitation.
- Data minimization and pseudonymization: Collecting only the necessary personal data and using pseudonymization techniques (replacing identifying information with pseudonyms) reduces the impact of potential breaches.
- Regular security testing: Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning help identify weaknesses in your security posture before they can be exploited by attackers.
Pros:
- Provides actual protection against data breaches: These measures are your first line of defense against cyber threats and data breaches.
- Creates evidence of compliance efforts: Documented security measures demonstrate your commitment to GDPR compliance and can be crucial in the event of an audit.
- Builds trust with customers and partners: Demonstrating strong data security practices builds trust and strengthens your reputation.
- May reduce severity of penalties if breaches occur: Evidence of robust security measures can mitigate penalties imposed by supervisory authorities in the event of a data breach.
Cons:
- Can require significant technical investment: Implementing robust security measures can involve costs associated with software, hardware, and personnel.
- May impact system performance or user experience: Some security measures, like encryption, can impact system performance or user experience if not implemented carefully.
- Requires regular updating as threats evolve: The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, requiring ongoing updates and adaptations to your security measures.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Deutsche Bank: Implemented comprehensive data loss prevention and encryption for all customer data.
- Vodafone: Introduced privacy-enhancing technologies, including differential privacy for analytics.
Actionable Tips:
- Conduct regular security risk assessments.
- Implement privacy by design in all new projects.
- Apply data minimization principles to reduce the scope of security efforts.
- Develop clear desk and clear screen policies.
- Implement multi-factor authentication for sensitive systems.
- Conduct regular penetration testing and vulnerability scanning.
- Document all security measures for accountability purposes.
Popularized By:
- ENISA (European Union Agency for Cybersecurity)
- National Cyber Security Centre (UK)
- ISO 27001 framework
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Technical and organizational security measures are not simply a "nice-to-have" but a fundamental requirement for GDPR compliance. They should be implemented from the outset of any project involving the processing of personal data and continuously reviewed and updated. This proactive approach is crucial for minimizing the risk of data breaches, demonstrating compliance, and maintaining the trust of your customers and partners.
7-Point GDPR Compliance Checklist Comparison
| Checklist Item | Implementation Complexity  |
Resource Requirements  |
Expected Outcomes  |
Ideal Use Cases  |
Key Advantages  |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Processing Inventory and Mapping | Medium to High – Requires cross-department collaboration and updates | Moderate – Staff time and data discovery tools | Visibility into data flows; compliance gap identification | Organizations needing comprehensive data oversight | Foundation for compliance; risk identification |
| Privacy Notices and Consent Management | Medium – Technical setup for consent tracking; iterative updates | Moderate to High – CMP platforms and legal expertise | Enhanced transparency; valid consent management | Organizations collecting direct user consent | Builds trust; reduces regulatory risk |
| Data Subject Rights Procedures | Medium to High – Workflow integration and tracking systems | Moderate – Systems for intake, tracking, training | Timely, compliant handling of DSARs; improved customer trust | Organizations receiving frequent data rights requests | Consistency and accountability; reduces response time |
| Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) | High – Specialized expertise and cross-functional involvement | Moderate to High – Legal, IT, privacy resources | Early risk detection; privacy by design adherence | High-risk processing projects or new systems | Prevents costly redesigns; regulatory compliance evidence |
| Data Breach Response Plan | Medium – Coordination and documentation processes | Moderate – Incident response team and training | Faster breach handling; minimized penalties; accountability | All organizations; critical for breach readiness | Reduces impact and regulatory penalties |
| Vendor Management and Data Processing Agreements | Medium to High – Contract review and ongoing monitoring | Moderate to High – Legal and compliance resources | Extended GDPR compliance through supply chain | Organizations relying on third-party processors | Clarifies responsibilities; legal recourse |
| Technical and Organizational Security Measures | High – Technical solutions and ongoing maintenance | High – Security technologies and expert personnel | Strong data protection; breach prevention | Organizations with sensitive data or high risk | Actual protection; may mitigate breach impact |
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Maintaining Your GDPR Compliance
This GDPR compliance checklist has covered essential aspects of establishing a robust data protection framework, from conducting data processing inventories and implementing data subject rights procedures to performing DPIAs and preparing for data breaches. Mastering these elements is not just about ticking boxes; it’s about building trust with your users, safeguarding your reputation, and avoiding hefty fines. Remember, the core components of GDPR compliance – data processing inventory and mapping, privacy notices and consent management, data subject rights procedures, DPIAs, a data breach response plan, vendor management, and technical and organizational security measures – are all interconnected and contribute to a holistic approach to data protection. By prioritizing these areas, you demonstrate a commitment to ethical data handling and create a more secure and transparent environment for everyone.
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and so are data privacy regulations. Regularly reviewing and updating your GDPR compliance program is paramount to staying ahead of the curve. This proactive approach ensures you remain compliant and reinforces your dedication to user privacy. Furthermore, choosing GDPR-compliant vendors plays a vital role in maintaining your own compliance posture.
To strengthen your GDPR compliance, particularly concerning data security and vendor management, consider Typewire, a secure email platform built with privacy and security by design. Typewire simplifies secure communication and collaboration while adhering to strict data protection principles. Visit Typewire today to discover how it can seamlessly integrate into your GDPR compliance strategy.
GDPR Compliance Checklist: Ensure Your Data Privacy Success
Posted: 2025-05-14
The 12 Best Email Clients for Mac in 2026: A Guide to Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-02-24
Professional Email Addresses: Your First Line of Defense for Trust and Security
Posted: 2026-02-21
How Do I Block Gmail and Reclaim Your Inbox Privacy
Posted: 2026-02-17
7 Top Canadian Tech Companies Leading in Privacy and Security for 2026
Posted: 2026-02-13
Professional Email Greeting: Master the professional email greeting today
Posted: 2026-02-10
What is Email Phishing: Securing Your Inbox Against Digital Fraud
Posted: 2026-02-06
10 Email Retention Policy Best Practices for Security and Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-02-03
Top 12 Secure Alternatives to Gmail for Privacy in 2026
Posted: 2026-01-31