Email Security for Small Business: Protect Your Data Now

Why Small Businesses Can't Ignore Email Security
Many small business owners believe they're too small to be targeted by cybercriminals. This is a dangerous misconception. Small businesses aren't just vulnerable; they are often the preferred targets. Cybercriminals view smaller companies as easier prey because of their often limited security resources and budgets.
Why Hackers Target Small Businesses
For example, a small business might lack a dedicated IT department to manage complex security systems. This makes implementing and maintaining strong email security protocols challenging. Also, small businesses often lack the funds to invest in comprehensive security solutions, leaving them exposed.
This vulnerability makes them attractive to cybercriminals seeking quick wins with minimal effort. A single compromised email can be devastating, threatening financial stability and customer trust. Understanding why email security is crucial for small businesses is paramount. Read more about why Email Security Matters.
The High Cost of Inaction
The impact of a security breach goes beyond the immediate financial losses. Small businesses are increasingly targeted by cyber threats, and email is a primary attack vector. In 2025, small businesses had the highest rate of targeted malicious emails at one in 323, including phishing, spam, and malware. This vulnerability is evident as 43% of all data breaches target small-to-medium-sized businesses (SMBs). It takes an average of 207 days to identify a breach—over half a year of potential damage. Find more detailed statistics here. Lost productivity, reputational damage, and legal issues can cripple a small business, potentially leading to closure. You might be interested in: How to master your business journey.
The Evolving Threat Landscape
The threats facing small businesses are constantly changing. Simple spam filters are no longer enough. Today's cybercriminals use sophisticated tactics like phishing, ransomware, and business email compromise (BEC) to exploit weaknesses. These attacks often target human error, using social engineering to trick employees into revealing sensitive data.

This means email security for small businesses is no longer optional; it's essential. Investing in robust email security isn't an expense; it's an investment in the long-term health and survival of your business.
The Evolving Threats Targeting Your Inbox
Cybercriminals are getting smarter. Their tactics now extend far beyond simple spam emails. They're designing attacks that can slip past standard security measures, aiming directly at the weak points of small businesses. Many of these attacks rely on human error, crafting malicious emails that look almost identical to legitimate messages.
Phishing: The Deceptive Art of Impersonation
Phishing remains a constant threat. Attackers impersonate trusted brands and people to steal login details and confidential information. These attacks use urgent language and attractive offers to trick people into clicking bad links or downloading infected files. For example, a phishing email might pretend to be from your bank, asking you to update your account details through a fake website.
These attacks often create a sense of urgency or use enticing offers. This psychological manipulation can trick individuals into taking actions that would be against their better judgment and compromise their security.
Business Email Compromise: Exploiting Trust
Business email compromise (BEC) attacks are especially dangerous. They target a company's financial processes and communication habits. Attackers might impersonate a CEO requesting a money transfer or a supplier sending a fraudulent invoice. These attacks exploit the trust built within business relationships, making them hard to spot. BEC attacks are often carefully planned to coincide with legitimate payment cycles.
Ransomware: Holding Your Data Hostage
Ransomware attacks continue to be a problem for businesses. They're often spread through seemingly harmless email attachments. Once opened, ransomware encrypts important data, locking it up until a ransom is paid. This can cause substantial financial losses and disrupt business operations. Downtime caused by ransomware can be costly, impacting productivity and customer trust.
To help understand these threats, let's look at a table outlining some common email risks:
Common Email Threats to Small Businesses: This table outlines prevalent email security threats targeting small businesses, their characteristics, and potential impact.
| Threat Type | How It Works | Warning Signs | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phishing | Impersonates legitimate entities to steal credentials | Unexpected requests for personal information, suspicious links, urgent language | Identity theft, financial loss, malware infections |
| Business Email Compromise (BEC) | Targets financial workflows and communication patterns | Unusual payment requests, changes in vendor communication, requests from unknown individuals | Financial loss, reputational damage, legal repercussions |
| Ransomware | Encrypts critical data and demands a ransom for its release | Suspicious attachments, system slowdowns, inability to access files | Data loss, financial loss, operational disruption |
This table provides a quick overview of some of the most common email threats that small businesses face. Recognizing these threats is the first step in protecting your organization.
The Rise of AI-Driven Threats
The world of email security is constantly changing. Cybercriminals are using new tactics and technologies. In 2025, phishing attacks grew by 28%, while AI-driven scams increased by a significant 67.4%, resulting in roughly $84 million in fraud losses. A worrying 94% of organizations said they experienced email security incidents, showing how widespread this problem is. You can learn more about these trends here. The rise of AI-powered attacks allows for highly personalized phishing campaigns designed just for your business. These AI threats can study how you communicate and create very convincing emails, making attacks more likely to succeed.
Remote Work: Expanding the Attack Surface
The move to remote work has made small businesses even more vulnerable to email threats. Employees accessing company networks from different locations and devices creates multiple entry points for cybercriminals. This highlights the need for strong email security for small business owners to protect their data and operations. Protecting your inbox is not just about data security; it's about protecting your business’s future.
What a Breach Really Costs Your Business

The initial expenses of an email security breach, like ransomware payments and system repairs, are only the beginning. The real cost goes much deeper and can affect your business for years. This includes major disruptions to your operations, resulting in lost revenue and reduced productivity. For example, if your systems are down due to ransomware, you can't fulfill orders, assist customers, or access essential data.
The Hidden Costs of Downtime and Recovery
Downtime is a serious consequence of a security breach. This lost time directly translates to lost revenue and lower productivity. Furthermore, restoring your systems and data can be a long and costly process, putting even more strain on your resources. This restoration frequently involves bringing in outside cybersecurity experts, buying new hardware or software, and implementing stronger security measures. This underscores the importance of strong email security, particularly for small businesses.
Furthermore, a breach can significantly damage your reputation. Customers lose faith in businesses that can't protect their data. This loss of trust can cause customer churn and make it challenging to acquire new clients. Rebuilding that trust can take years and involve substantial investment in PR and marketing. Understanding and mitigating these threats is essential. You can find out more about effective strategies in this resource on phishing awareness training.
The Long-Term Impact on Customer Trust
Losing customers isn't the only consequence of a tarnished reputation. Negative reviews and media attention can further harm your brand image, making it even tougher to recover. This negative publicity can also affect your ability to secure funding or attract investors. This shows how the effects of a breach reach far beyond the immediate financial loss, impacting your long-term growth and viability.
Regulatory Penalties and Legal Ramifications
In addition to reputational damage, you might face legal and regulatory repercussions. Depending on the specifics of the breach and the type of data compromised, you could be subject to substantial fines and lawsuits. These penalties can be especially damaging for small businesses, which often operate with smaller budgets. The repercussions of insecure email channels can be devastating. In fact, 60% of small businesses shut down within six months of a cyberattack or data breach. Small businesses are also three times more likely to be targeted than larger enterprises, with 70% of cyberattacks aimed directly at them, costing an estimated $2.4 billion annually. Learn more about relevant cybersecurity statistics. Investing in robust email security for your small business isn't a luxury anymore—it's essential for survival.
Protection Strategies That Won't Break Your Budget
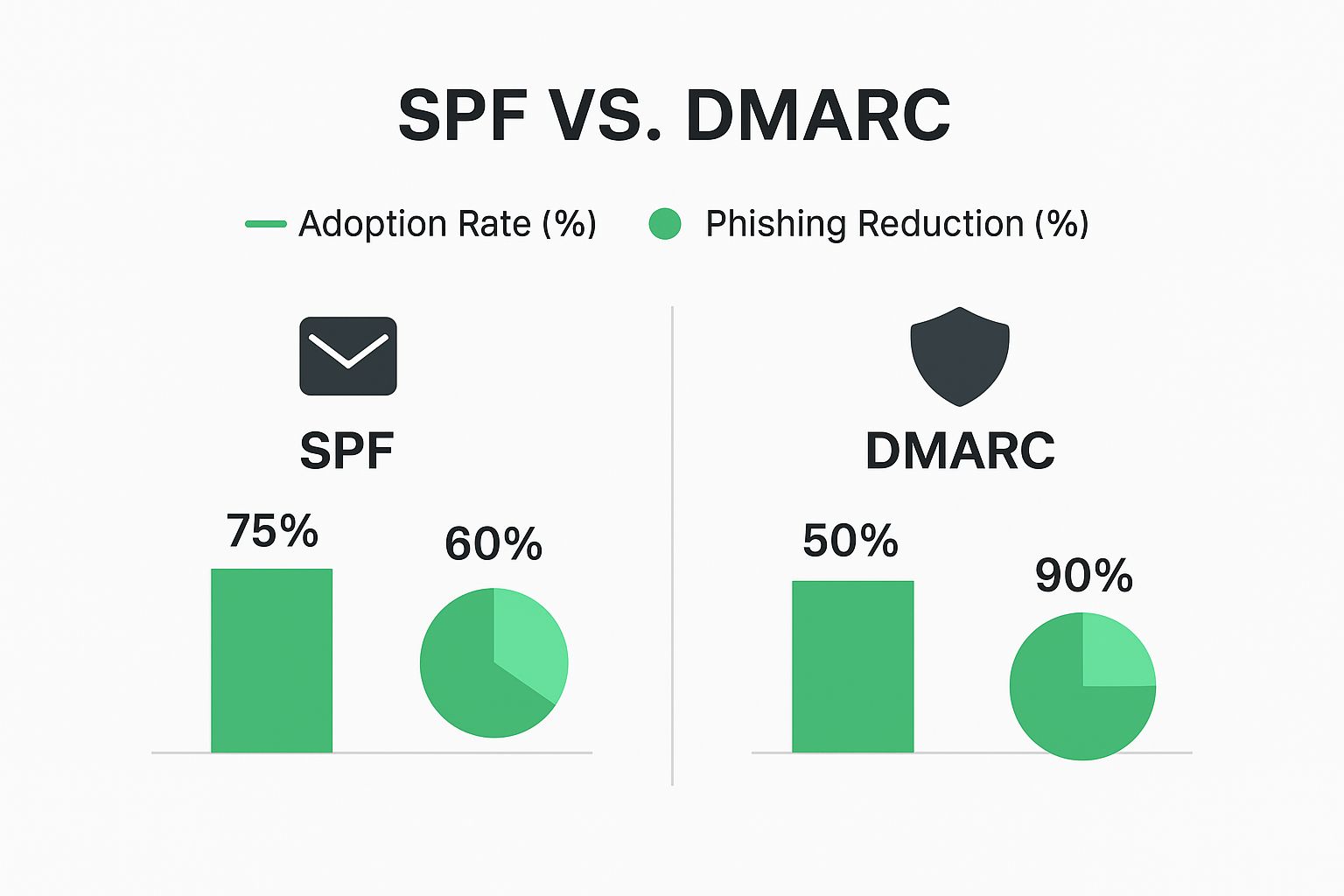
The infographic above illustrates how two key email authentication protocols—SPF and DMARC—are adopted and how effective they are at reducing phishing. While 75% of organizations use SPF, resulting in a 60% reduction in phishing, DMARC, adopted by 50%, boasts a far more impressive 90% phishing reduction rate. This highlights the power of DMARC, especially for small businesses looking to enhance their security. This section explores budget-friendly email protection strategies tailored for smaller operations. We'll focus on practical, layered defenses that offer robust protection without the high cost of complex enterprise solutions.
Essential Email Authentication Protocols
Protecting your business from email spoofing starts with implementing strong email authentication protocols. These protocols verify the sender's identity, making it difficult for attackers to impersonate your business. This protects your brand reputation and prevents customers from falling prey to phishing scams.
-
SPF (Sender Policy Framework): SPF specifies which mail servers are allowed to send emails from your domain, preventing unauthorized senders from using your domain for fraudulent emails.
-
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): DKIM digitally signs your emails, verifying their authenticity and preventing tampering in transit. It's like a digital seal of approval for your messages.
-
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance): DMARC works with SPF and DKIM, telling receiving mail servers what to do with emails that fail authentication checks. This actively blocks spoofed emails from reaching your customers' inboxes.
Setting up these protocols may seem technical, but many email providers offer simple setup guides and assistance. These protocols are essential for a solid email security foundation, particularly for small businesses.
Encryption: Shielding Your Sensitive Data
Encryption is another vital component of small business email security. Encryption scrambles your email content, making it unreadable to anyone but the intended recipient. This is critical when sending confidential data like financial information or customer details.
-
TLS (Transport Layer Security): TLS encrypts emails in transit between mail servers, protecting them as they travel across the internet. It's like sending your message in a secure envelope.
-
End-to-End Encryption: This method encrypts emails on the sender's device and decrypts them only on the recipient's device, offering the highest level of security. It's like having a private conversation with a secret code.
Evaluating Solutions Based on Your Needs
When it comes to email security, there's no single perfect solution. The best approach depends on your specific business type, industry risks, and budget. A small online retailer handling sensitive customer data will have different security needs than a local consulting firm.
To help you choose the best fit for your needs, we've compiled a comparison table outlining various email security options:
Email Security Solutions Comparison for Small Businesses
This table compares different email security approaches suitable for small businesses based on protection level, cost factors, and implementation difficulty.
| Security Solution | Protection Level | Cost Range | Implementation Complexity | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Email Provider Security | Low | Included with email service | Low | Very small businesses with limited budgets |
| Enhanced Email Security Add-ons | Medium | $2-$10/user/month | Low to Medium | Businesses needing improved security without significant investment |
| Dedicated Email Security Gateways | High | $10-$50/user/month | Medium to High | Businesses with high security requirements and IT resources |
| Enterprise-Grade Email Security Suites | Very High | $50+/user/month | High | Large organizations with complex security needs |
As you can see, there's a wide range of solutions available. The right one for you depends on your specific circumstances. Consider factors such as the technical expertise required for setup and maintenance, the level of customer support provided, and the scalability of the solution to accommodate your business's future growth.
By carefully considering these factors and comparing different options, you can create a cost-effective email security strategy that provides optimal protection without straining your budget. Implementing a combination of authentication protocols and encryption methods greatly enhances your email security posture and protects your business from emerging online threats.
Turning Employees Into Your Security Front Line

Your employees represent both a significant security vulnerability and a crucial line of defense for your small business's email security. This duality highlights the critical importance of transforming employee behavior. Instead of viewing your team as a potential weakness, successful small businesses empower them to become security assets. This transformation involves practical, engaging training that equips employees to actively protect sensitive company data. You can learn more at Typewire.
Training That Addresses Real-World Threats
Effective security training goes beyond general guidelines. It should address the specific threats your employees face daily, such as increasingly sophisticated phishing attacks that closely mimic legitimate communications. Employees also need clear guidance on handling sensitive customer information, particularly given the increasing importance of data privacy regulations. Interactive simulations can be a valuable training tool, allowing employees to practice identifying phishing emails and learn how to report suspicious activity.
Simulation Testing: Identifying Vulnerabilities Without Blame
Regular simulated phishing tests are essential for uncovering vulnerabilities in your security posture. However, it's vital to conduct these tests in a constructive, blame-free environment. Employees should understand the purpose of the exercise, which is to identify weaknesses and provide targeted training, rather than to single out individuals. This proactive approach significantly strengthens your defenses compared to reacting after a breach.
Building a Security-Minded Culture
Robust email security hinges on a company culture where everyone shares responsibility for security. This requires moving beyond mere compliance and fostering active engagement in security best practices. Employees should feel comfortable reporting suspicious emails without fear of reprisal. Security measures should be user-friendly, not obstacles that employees try to bypass. When employees understand the reasons behind security protocols, they're much more likely to adopt them. This shift in mindset creates a potent "human firewall" against evolving email threats.
Practical Steps for Empowering Your Team
Here are some practical steps to empower your team and strengthen your security posture:
- Regular Training: Conduct frequent, concise training sessions with a focus on real-world examples and interactive exercises.
- Clear Policies: Develop and clearly communicate easy-to-understand security policies.
- Open Communication: Establish channels for employees to report suspicious activity without hesitation or fear of judgment.
- Positive Reinforcement: Recognize and reward employees who demonstrate strong security practices.
- Ongoing Education: Keep abreast of emerging email threats and adapt your training accordingly.
By investing in your employees' security awareness, you invest in the overall security and resilience of your small business. A well-trained team becomes a powerful, proactive defense against the constantly evolving landscape of email threats. This not only safeguards your valuable data but also contributes to a stronger, more secure organization.
Your 90-Day Email Security Transformation Plan
Transforming your small business's email security doesn't necessitate a complete system overhaul. A focused, gradual approach is all you need. This 90-day plan offers a practical roadmap, especially for small businesses with limited resources, balancing immediate needs with long-term security objectives. We'll guide you through a simple vulnerability assessment and help you prioritize the most effective protections for your specific business model.
Phase 1: Assessment and Quick Wins (Days 1-30)
The first 30 days concentrate on understanding your current vulnerabilities and implementing fundamental protections. This involves a straightforward self-assessment to pinpoint your weaknesses and prioritize quick, high-impact security enhancements.
-
Vulnerability Assessment: Begin by evaluating your existing email practices. Do you have basic spam filters in place? Are your employees trained to identify phishing emails? This assessment will highlight areas requiring immediate attention.
-
Implement Basic Authentication: Set up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These protocols are essential for preventing email spoofing and are typically easy to implement with your email provider. Learn more about SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
-
Enforce Strong Passwords: Mandate strong, unique passwords for all email accounts. Implement a password manager to assist employees in securely managing their credentials. This simple step significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
-
Initial Security Awareness Training: Conduct a basic security awareness training session for your team. Focus on recognizing common phishing tactics and the importance of reporting suspicious emails. This initial training establishes a security-conscious foundation.
Phase 2: Building Stronger Defenses (Days 31-60)
The second phase focuses on bolstering your defenses and implementing more advanced security measures. This includes enhancing your technical protections and developing more robust employee training programs.
-
Explore Advanced Threat Protection: Consider incorporating advanced threat protection into your email security setup. This might involve upgrading your current email provider or investing in a dedicated email security gateway. These solutions can help identify and block more sophisticated attacks.
-
Implement Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA on all email accounts. This adds an extra layer of security, even if passwords are compromised.
-
Advanced Security Awareness Training: Conduct more comprehensive security training. Focus on real-world examples of phishing and other email threats. Consider using simulated phishing tests to evaluate employee understanding and reinforce what they've learned.
-
Develop Security Policies: Create clear, written security policies that address email usage, data handling, and incident response procedures. Documenting these procedures ensures everyone understands their responsibilities.
Phase 3: Continuous Improvement and Long-Term Security (Days 61-90)
The final phase centers on establishing a culture of continuous improvement and ensuring your email security remains robust over the long term.
-
Regular Security Assessments: Perform regular security assessments to identify emerging vulnerabilities and adapt your strategies accordingly. This is similar to regular car maintenance—it keeps everything running smoothly.
-
Ongoing Training and Education: Provide regular security awareness refreshers for your team. Keep them informed about new threats and best practices. This reinforces a security-minded culture.
-
Refine Incident Response Plan: Develop and routinely test your incident response plan. This ensures your team knows how to react swiftly and efficiently in the event of a security incident.
-
Review and Update Security Policies: Regularly review and update your security policies to stay current with evolving threats and best practices. Consistent policy maintenance ensures lasting protection.
This 90-day plan provides a structured approach to enhancing email security for your small business. By following these steps, you'll considerably reduce your vulnerability to email threats, protect your valuable data, and establish a more secure foundation for your business's future. Ready to take control of your email security and protect your business? Start your free trial of Typewire today: Typewire Secure Email
Email Security for Small Business: Protect Your Data Now
Posted: 2025-05-24
How to Send an Encrypted Email and Protect Your Digital Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-23
Email Hosting Canada The Definitive Guide to Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-01-20
How to Send Email Securely: A Guide to Real Privacy & Security
Posted: 2026-01-16
Why Am I Getting So Many Junk Emails? A Guide to Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-13
How to Disable Email Tracking and Protect Your Email Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-09
Secure Email Services: A Guide to True Email Privacy and Security
Posted: 2026-01-06
How to Create a Personal Email Domain for Ultimate Email Security and Privacy
Posted: 2026-01-02
Best email hosting for small business: Top options & comparisons
Posted: 2025-12-31